A Collateral after Splenic Vein Thrombosis
Case Report
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v8i1.14Keywords:
collaterals, splenic vein thrombosis, CT-angiographyAbstract
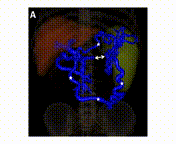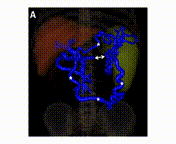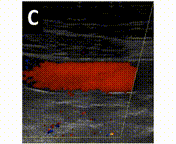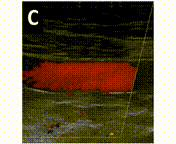
A 46-year-old man presented to the emergency department because of relapsing abdominal pain in the left abdominal quadrants. At admission, he was in good general condition and his vital signs were normal. The only abnormal laboratory findings were a C-reactive protein of 30 mg/L and thrombocytes of 127 G/L. An abdominal computed tomography (CT) scan showed a thrombosis of the distal splenic vein (panel A, double arrow) with the presence of a superior and an inferior spleno-mesenteric collateral (panel A, asterisks). The axial CT scan (panel V, arrows) and Doppler sonography (panel C) showed that the thick collaterals developed below the abdominal wall. A gastroscopy showed stage I fundic varices, but no esophageal varices. (1-10) This patient was diagnosed with a smoldering multiple myeloma 5 years earlier with regular follow-up in the hemato-oncology department. No other pro-thrombotic conditions were found and in a follow-up CT scan 6 months later the findings were un-changed despite anticoagulation. Splenic vein thrombosis is frequently diagnosed in the chronic stage, when collaterals have already developed (11-18). In this case, the presence of two major spontaneous shunts between the splenic vein and the superior mesenteric vein is preventing complications (19-23) such as porto-systemic encephalopathy and variceal bleeding
References
Vidal-Gonzalez J, Martinez J, Mulay A, et al. Evolution of spontaneous portosystemic shunts over time and following aetiological intervention in patients with cirrhosis. JHEP Rep 2024;6(2):100977. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhepr.2023.100977.
Obmann VC, Ardoino M, Klaus J, et al. MRI Extracellular Volume Fraction in Liver Fibrosis-A Comparison of Different Time Points and Blood Pool Measurements. J Magn Reson Imaging 2024. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.29259.
Mansour N, Sirtl S, Angele MK, Wildgruber M. Management of Sinistral Portal Hypertension after Pancreatico-duodenectomy. Dig Dis 2024;42(2):178-185. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1159/000535774.
Karlsen TH, Rutter H, Carrieri P, et al. The EASL-Lancet Commission on liver health in Europe: prevention, case-finding, and early diagnosis to reduce liver-related mortality. Lancet 2024;403(10436):1522-1524. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00204-6.
Ferraioli G, Barr RG, Berzigotti A, et al. WFUMB Guidelines/Guidance on Liver Multiparametric Ultrasound. Part 2: Guidance on Liver Fat Quantification. Ultrasound Med Biol 2024. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2024.03.014.
Dong Y, Wang WP, Zadeh ES, et al. Comments and illustrations of the WFUMB CEUS liver guidelines: Rare benign focal liver lesion, part I. Med Ultrason 2024;26(1):50-62. DOI: https://doi.org/10.11152/mu-4260.
Delgado MG, Mertineit N, Bosch J, Baumgartner I, Berzigotti A. Combination of Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) and Sarcopenia predicts mortality after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS). Dig Liver Dis 2024. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dld.2024.03.003.
Zbinden L, Catucci D, Suter Y, et al. Automated liver segmental volume ratio quantification on non-contrast T1-Vibe Dixon liver MRI using deep learning. Eur J Radiol 2023;167:111047. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2023.111047.
Vikhe VB, Khandol D, Garud AA. A Young Male With Non-cirrhotic Cryptogenic Portal Cavernoma: An Authoritative Case Study. Cureus 2023;15(12):e50570. DOI: https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.50570.
Tang R, Wu G, Yu Q, et al. Location and extent of cavernous transformation of the portal vein dictates different visceral side revascularization in Meso-Rex bypass. BMC Surg 2023;23(1):276. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12893-023-02168-3.
Felli E, Selicean S, Guixe-Muntet S, et al. Mechanobiology of portal hypertension. JHEP Rep 2023;5(11):100869. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhepr.2023.100869.
Cathomas M, Mueller F, Mertineit N, et al. Comparison of transarterial bland embolization and drug-eluting beads transarterial chemoembolization for very early and early hepatocellular carcinoma not amenable for surgery or ablation: a single center retrospective data analysis. J Gastrointest Oncol 2023;14(5):2167-2177. DOI: https://doi.org/10.21037/jgo-23-261.
Zhao JW, Cui XH, Zhao WY, et al. Acute mesenteric ischemia secondary to oral contraceptive-induced portomesenteric and splenic vein thrombosis: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022;10(29):10629-10637. DOI: https://doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i29.10629.
Renzulli M, Dajti E, Ierardi AM, et al. Validation of a standardized CT protocol for the evaluation of varices and porto-systemic shunts in cirrhotic patients. Eur J Radiol 2022;147:110010. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2021.110010.
Nery F, Carneiro P, Correia S, et al. Systemic inflammation as a risk factor for portal vein thrombosis in cirrhosis: a prospective longitudinal study. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2021;33(1S Suppl 1):e108-e113. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/MEG.0000000000001982.
Chen BB, Mu PY, Lu JT, et al. Sinistral portal hypertension associated with pancreatic pseudocysts - ultrasonography findings: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021;9(2):463-468. DOI: https://doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i2.463.
Rana SS, Sharma R, Ahmed SU, Gupta R. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided transmural drainage of walled-off pancreatic necrosis in patients with portal hypertension and intra-abdominal collaterals. Indian J Gastroenterol 2017;36(5):400-404. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12664-017-0792-y.
Arslan S, Onur MR, Akpinar E. A rare cause of upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage: chronic thrombosis of the splenic artery. Turk J Gastroenterol 2017;28(3):221-222. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5152/tjg.2017.16745.
Sule A, Borja A, Chin TJ. Progression of Thrombus in Portal Vein, Superior Mesenteric Vein, and Splenic Vein Even on Anticoagulation in a Patient with Ascending Colonic Malignancy with Liver Metastasis: Portal Vein Thrombosis versus Portal Vein Tumor Thrombosis. Int J Angiol 2016;25(5):e97-e99. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1544125.
McIntyre B, Marsh M, Walden J. Puzzles in practice: splenic vein thrombosis. Postgrad Med 2016;128(5):538-40. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/00325481.2016.1185922.
Novelli PM, Cho K, Rubin JM. Sonographic assessment of spleen stiffness before and after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt placement with or without concurrent embolization of portal systemic collateral veins in patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension: a feasibility study. J Ultrasound Med 2015;34(3):443-9. DOI: https://doi.org/10.7863/ultra.34.3.443.
Tang J, Abbas J, Hoetzl K, et al. Ligation of superior mesenteric vein and portal to splenic vein anastomosis after superior mesenteric-portal vein confluence resection during pancreaticoduodenectomy - Case report. Ann Med Surg (Lond) 2014;3(4):137-40. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amsu.2014.08.001.
Dragoteanu M, Balea IA, Piglesan CD. Nuclear medicine dynamic investigations in the diagnosis of Budd-Chiari syndrome. World J Hepatol 2014;6(4):251-62. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v6.i4.251.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Martin Maurer, Andrea De Gottardi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This license requires that reusers give credit to the creator. It allows reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format, even for commercial purposes.