Archives
-

Human and Artificial Intelligence in Radiology - Radiographers’ Perceptions of Artificial Intelligence and Theranostics - Optic Nerve Sheath Meningocele - Visual Journey through Tuberous Sclerosis Complex - Effect of Sedation on MRI-Based Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter Measurements in Children - Management of a Bone Metastasis from Thyroid Carcinoma - Impact of Diabetes and Diabetic Kidney Disease on Bone Mineral Density - Multivessel Transcatheter Arterial Embolization to Treat Hip Osteoarthritis
Vol. 27 No. 1 (2026)Russian Federation - Human and Artificial Intelligence in Radiology: Current Status, Evidence, Regulation, and Future Perspectives
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v27i1.14
Zainab Magomedova1,2, Ekaterina S. Pershina1,2, Keivan Daneshvar3, Gerd Nöldge3, Frank Mosler3
Artificial intelligence (AI) has rapidly evolved into a transformative force in radiology, complementing human intelligence across the entire imaging workflow. Current applications range from image acquisition and reconstruction to automated detection, quantification, triage, and clinical decision support. Evidence to date demonstrates that AI systems can match or exceed human performance in narrowly defined tasks, particularly in pattern recognition and workflow optimization. However, robust prospective validation, demonstration of clinical impact, and proof of generalizability across institutions and populations remain limited.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Chile - Optic Nerve Sheath Meningocele: a case report and review of the literature
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v27i1.16
Ilson Sepúlveda Aguilar1*, Francisco Rivas-Rodriguez2
Optic nerve sheath meningocele (ONSM) is a rare condition with only a few cases reported in the medical literature. The etiology is unknown. The condition is characterized by an expansion of the cerebrospinal fluid space surrounding the optic nerve, without associated inflammation or the presence of orbital or cerebral neoplasms at the apex of the orbit. The condition is characterized by the absence of specific symptoms, with the most common being blurred vision and retro-orbital pain. We present the case of a young patient who was admitted to the emergency department at an external hospital. A clinical examination revealed painless right exophthalmos. No additional neurological symptoms were observed. A Computed Tomography (CT) scan and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) revealed an ONSM.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v27i1.18
Onwuzu, Sobechukwu W I1; Uche-Nwankwo, Adanna Munachimsoaga1*; Ozoamalu, Chinemerem Sebastian1; Ozohili, Chikaosolu Vanessa1; Peter-Adim, Ezinne Stacey1; Solomon, Prisca Chinecherem1; Sopuluchukwu, Precious Ogechi1; Onwunta, Ikechukwu Emmanuel1
1Department of Medical Radiography and Radiological Sciences, University of Nigeria
Nigerian radiographers demonstrate moderate familiarity with AI but limited understanding of theranostics. While job security concerns persist, willingness to upskill is strong. Structured training, mentorship, and curriculum reform are essential to support professional adaptation and safeguard radiographers’ relevance in the era of AI and theranostics.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
India - Visual Journey through Tuberous Sclerosis Complex: Multisystem Imaging Insights
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v27i1.20
Thiagarajan Veerappan1, Geetha Ganesan1, Kalpana Sivalingam1
1Barnard Institute of Radiology, Madras Medical College, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
Tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) is a rare genetic disorder affecting several systems, characterized by hamartomatous lesions in the brain, kidneys, lungs, skin, and bones. Imaging plays a pivotal role in diagnosis and management. We report a case series of four patients exhibiting diverse clinical manifestations who received multimodal imaging from 2022 to 2024. The imaging findings were aligned with clinical and diagnostic criteria established by the 2012 International TSC Consensus guidelines. The cases had distinctive radiological characteristics of TSC, encompassing subependymal nodules, subependymal giant cell astrocytomas (SEGAs), renal angiomyolipomas, pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM), cutaneous lesions, and skeletal anomalies. Cross-sectional imaging facilitated precise diagnosis and directed therapies, including embolization, for renal pseudoaneurysms. The series highlights the significance of a thorough imaging strategy in recognizing both typical and incidental characteristics of TSC. Prompt identification enables swift diagnosis, focused treatment, and long term surveillance.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v27i1.22
Omair Ashraf Shah1, Mudhabir Ashraf2, Akib Arfee1*, Sumaira Maqbool3
1Department of Radiodiagnosis and Imaging, Govt. Medical College Srinagar, India
2Department of Anaesthesia and Critical Care, Govt. Medical College Srinagar, India
Sedation significantly influences ONSD measurements on MRI in pediatric patients. These findings highlight the need for careful consideration of sedation status when using ONSD as a surrogate for ICP. Age-related trends further highlight the importance of using adjusted reference values.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v27i1.24
Halima Batani1*, Hafsa Bensimimou1, Abdel Amide Gbadamassi1,2, Zakaria Ouassafrar1, Amal Guensi1
1Nuclear Medicine Department, Ibn Rochd University Hospital Center, Casablanca, Morocco
[18F]FDG PET/CT is an essential tool in the diagnostic and therapeutic evaluation of poorly differentiated follicular-origin thyroid carcinomas. Its contribution is pivotal in guiding clinical decision-making. Moreover, surgical management of isolated bone metastases can offer a genuine opportunity for durable disease control.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v27i1.26
Surjeet Chandail1, Arshed Hussain Parry1*, Majid Jehangir1, Syeed Aalishan Fatima1, Seema Qayoom2
Patients with T2DM, particularly those with concomitant CKD, exhibit a substantially higher prevalence of osteopenia and osteoporosis compared to non-diabetic individuals. These findings emphasize the need for routine bone health assessment and early osteoporosis screening in diabetic patients to reduce fracture risk and improve clinical outcomes.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
USA - Multivessel Transcatheter Arterial Embolization to Treat Hip Osteoarthritis: A Pilot Case Series
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v27i1.28
Prem Krishnamurthy1*, Nishanth Konduru1, Siddhartha Rao1
1Rao Clinic, Cary, North Carolina, United States
Chronic hip pain due to osteoarthritis (OA) is a prevalent source of disability in older adults. While total hip arthroplasty (THA) remains the standard treatment for end-stage disease, many patients are not surgical candidates due to comorbidities or personal preferences. Transcatheter Arterial Embolization (TAE) of the hip has emerged as a minimally invasive treatment for OA-related pain, but further evidence is warranted to establish its role in treatment pathways.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
A survey of the standard radiation protection practice in radiography departments of some-selected tertiary hospitals in south east Nigeria - Case report of a non-functional ectopic kidney in crossed fused renal ectopia on [99mTc] Tc-DMSA renal rcintigraphy: A rare entity - Diagnostic accuracy of 18F-NaF PET/CT vs 99mTc bone scintigraphy for detection of skeletal metastases: A systematic review and meta-analysis of head-to-head studies - Ectopic thyroid in the anterior mediastinum coexisting with a normally positioned thyroid gland in neck: Case report - A case of ovarian NIFTP treated with iratherapy
Vol. 25 No. 1 (2025)https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v25i1.14
Ezenwaka, Augusta Amarachi*1,ORCID; Ibe, Chijioke K.1; Ezugwu, Wisdom K.1; Ifeanyi, ThankGod O.1; Nwadike, Uchechukwu I.1
The radiation protection practices implemented in the radiology departments of tertiary hospitals in southeastern Nigeria have a significant impact on the safety of patients, healthcare professionals, and the general public. However, there is a lack of comprehensive understanding regarding adherence to standard radiation protection protocols in these departments.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v25i1.18
Zakaria OuassafrarORCID1, Abdel Amide GbadamassiORCID1,2, Halima BataniORCID1,
Hafsa Bensimimoun1, Amal GuensiORCID1
1Nuclear Medicine Department, Ibn Rochd University Hospital Center, Casablanca, Morocco
Crossed fused renal ectopia is a rare congenital malformation, with an estimated incidence of 1 in 7'500 live births. It occurs more frequently in males and represents the second most common renal fusion anomaly after the horseshoe kidney. Renal scintigraphy with [⁹⁹ᵐTc]Tc-DMSA remains the most reliable method for confirming the diagnosis and assessing renal function.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v25i1.16
Tosif Quazi1, Haroon Rashid*1, Aamir Majeed Shah1
NaF PET/CT demonstrates significantly higher sensitivity, specificity, and overall diagnostic accuracy than 99mTc bone scintigraphy for detecting skeletal metastases across malignancies. Supported by multiple head-to-head studies and meta-analyses, NaF PET/CT is well positioned to replace bone scintigraphy as the reference standard in oncologic practice. Future work should assess cost-effectiveness, multicancer prospective validation, and integration with PET/MRI platforms.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v25i1.20
Arshed Hussain Parry MD*1, Zahia Shabir MBBS1, Pirzada Mohammad Suhaib MD1, Irfan Yousuf Wani DM2, Mir Wajahat Un Nazir, MD3, Shabir Ahmad Bhat, MD1
¹Department of Radiodiagnosis, Government Medical College, Srinagar, Jammu & Kashmir, India
2Department of General Medicine, Government Medical College, Srinagar, Jammu & Kashmir, India
3Department of Pathology, Government Medical College, Srinagar, Jammu & Kashmir, India
This case underscores the importance of considering ectopic thyroid tissue within the anterior mediastinum in the differential diagnosis of anterior mediastinal masses, which more commonly include thymic tumors, germ cell tumors, and lymphomas.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Morocco - A case of ovarian NIFTP treated with iratherapy
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v25i1.22
E. Kpekpeou1, A. Muhoza1, S. Chkikar1, M. Goudira1, A. El Boukhrissi1, N. Ismaili Alaoui1
¹Nuclear Medicine Department, Hassan II University Hospital Center, Fès, Morocco
Struma ovarii is a form of mature monodermal teratoma, a rare germ cell tumor containing more than 50% thyroid tissue. Its transformation into a malignant tumor is rare. NIFTP (non-invasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary nuclear features) is an entity characterized by a completely encapsulated follicular proliferation with papillary nuclear features, but without invasion or high-risk criteria. It has an excellent prognosis when located in the thyroid gland. Its presence in the struma ovarii makes its prognosis uncertain. We report a case of ovarian NIFTP treated with complementary iodine-131 isotope therapy.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-

A Case of Radiation-induced Differentiated Thyroid Cancer - Pediatric Ovarian Torsion at Two Years of Age: A Rare Gynecological Emergency - From Fibroscan to 2D Shear Wave Elastography: Technological Evolution or Diagnostic Substitution in Liver Fibrosis Assessment? - Comparison of diagnostic performance of CT with rectal contrast vs. CT with rectal and intravenous contrast for the diagnosis of acute appendicitis - Unusual Pattern of Violation of Weigert Meyer Rule with Ureterocele in an Adult: A Case Report and Literature Review with Review of Associated Embryology
Vol. 26 No. 1 (2025)https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v26i1.14
Sharma, Rohin1ORCID; Batra, Radhika1; Pradhan, Gaurav S1; Ebinesh Arulnathan2ORCID
¹Department of Radiodiagnosis, Maulana Azad Medical College, Bahadur Shah Zafar Marg, Delhi, India
2Department of Radiology, Alder Hey Children’s NHS Foundation Trust, Liverpool- L14 5AB, UK
Radiologists and urologists should bear in mind the possibility of these violations when dealing with patients with a duplex system. Furthermore, patients with congenital urinary tract anomalies may present primarily in adulthood and have an uneventful childhood.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v26i1.18
Aslan, Ahmet*1, Parry, Arsheed Hussain1,2, AlAli, Muhammed Taher1, Alsaleh, Banoo Loai1, Almutawea, Abdulaziz3, Bakry, Husham3, Juma, Isam Mazin3
¹Department of Radiology, King Hamad University Hospital, Busaiteen, Al Muharraq, Bahrain
2Department of Radiodiagnosis, Government Medical College, Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir, India
3Department of Surgery, King Hamad University Hospital, Busaiteen, Al Muharraq, Bahrain
CT-RC proved to be as accurate as CT-IVRC in the diagnosis of AA. CT with rectal contrast alone could be performed in suspected cases of AA particularly in patients with contraindications to intravenous contrast administration.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v26i1.16
Akib Arfee1, Omair Ashraf Shah1, Asif Iqball2, Afshana Bashir3, Aaqib Manzoor*1
¹Department of Radiodiagnosis and Imaging, Govt. Medical College Srinagar, India
2Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Govt. Medical College Srinagar, India
3Department of Pathology, Govt. Medical College Srinagar, India
2D SWE matches Fibroscan’s accuracy but with fewer failures and advantage of real time anatomical guidance, making it a viable alternative especially for obese or ascitic CLD patients
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Bahrain - Pediatric Ovarian Torsion at Two Years of Age: A Rare Gynecological Emergency
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v26i1.20
Mujahed Abdul Sattar Raheem1, Arshed Hussain Parry*1, Hussam Hassan Ismail1, Wael Hamed Ibrahim1, Martin Corbally1
¹Department of Radiology, King Hamad University Hospital, Busaiteen, Al Muharraq, Bahrain
This case report discusses the diagnosis of pediatric ovarian torsion including risk factors, symptoms, imaging modalities, and surgical diagnostics to improve diagnosis and shorten time to treatment. In addition, this case supports the use of laparoscopy for diagnosis of ovarian torsion if indicated by clinical suspicion and supplemental imaging studies.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Morocco - A Case of Radiation-induced Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v26i1.22
Arnauld Muhoza1*, Esso-Mada Kpekpeou1, Maha Chaoui1, Aicha El Boukhrissi1, Nadia Ismaili Alaoui1
¹Nuclear Medicine Department, Hassan II University Hospital Center, Fès, Morocco
The association between differentiated thyroid cancer and exposure to ionizing radiation has been well-known since the radioactive fallout of the 20th century [1]. Follow-up consultations after radiotherapy must address three major objectives: the assessment of oncological response, the evaluation of acute or late toxicity to ionizing radiation, and the screening for a second cancer [2]. Surveillance is especially indicated for cases with external irradiation such as patients with a history of cervical, upper mediastinal, craniospinal, or total body radiotherapy, in addition to internal contamination exposures due to nuclear accidents. This risk is limited to the development of differentiated thyroid cancer, namely papillary or follicular types [2]. In fact, the risk is highest for irradiation received before the age of five and decreases with age, becoming non-significant if irradiation takes place after 15 to 20 years of age [3].We report a case of radiation-induced papillary thyroid carcinoma in a 16-year-old adolescent, managed in the Nuclear Medicine Department at Hassan II-Fez University Hospital Center.
-
Importance of Molecular Imaging Characteristics for the Diagnosis and Management of Tumor-induced Osteomalacia - Eccentric Case of Thoracic Spinal Hemangioma Masquerading as Cauda Equina Syndrome - Sporadic Case of LGI1 Autoimmune Encephalitis Feigning as Basal Ganglia Stroke: Exhuming its Pathophysiologic Basis - Importance of Molecular Imaging Characteristics for the Diagnosis and Management of Tumor-induced Osteomalacia - Contribution of [18F] FDG PET/CT in the Diagnosis of Prosthetic Valve Infective Endocarditis
Vol. 24 No. 1 (2025)USA - Eccentric Case of Thoracic Spinal Hemangioma Masquerading as Cauda Equina Syndrome
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v24i1.14
We present a case of spinal hemangioma with clinical presentation with lower limb weakness, loss of sensation, back pain, urinary retention and difficulty in bowel movements for 9 months. Patients presenting with lumbar myeloradiculopathy should be carefully evaluated to distinguish it from cauda equina syndrome, spinal dural fistula, spinal cord tumors, and metastasis. Evaluation including MRI brain and CT scan lumbar spine were within normal limits. Further workup including CT scan and MRI thoracic spine revealed T5 vertebral body spinal hemangioma with spina cord compression at T5-T6. The main pathology here is slowly progressive tumor that had power to scrunch the spinal cord and shatter the vertebra, thereby ushering the onset of myeloradiculopathy. Neurosurgery was consulted and they decided to perform a preoperative embolization, and surgical decompression. Recurrence of symptoms despite surgical intervention might necessitate administration of radiation therapy. The neuronal recovery following surgery might be prolonged given the degree of spinal cord injury.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
USA - Sporadic Case of LGI1 Autoimmune Encephalitis Feigning as Basal Ganglia Stroke: Exhuming its Pathophysiologic Basis
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v24i1.16
LGI1 encephalitis is an immune mediated neurological disorder effecting temporal lobe and basal ganglia. The classic clinical syndrome comprises of myoclonic jerks of the ipsilateral upper arms, facial twitching, memory disturbances, behavioral disturbances and hyponatremia. With its overarching symptoms, it does not snug perfectly with either seizure or movement disorder. The main pathological basis is mass production of anti-LGI1 auto-antibodies which strike the LGI1 protein in the neuronal milieu and presynaptic membrane. On grounds of this immune mediated onslaught, LGI1 protein injury transpires and slowing of signal conduction at the synaptic interface never ensues. In patients with aforementioned symptoms, a high degree of clinical suspicion necessitate MRI brain imaging which shows T2 hyperintensity in basal ganglia, temporal lobe and frontal lobe. This can be corroborated with assessing LGI1 antibody levels in the blood and CSF to monitor disease progression as well as treatment response. As soon as diagnosis is confirmed, intravenous corticosteroids, intravenous immunoglobulins or plasma exchange will reverse the epileptic activity and cognitive dysfunction. Long term immunosuppressive therapy is warranted as it is inclined to reduce the onset of temporal lobe epilepsy and hippocampal atrophy. Regular follow up to detect new clinical symptoms and brain lesions is recommended in these patients to reduce morbidity and mortality.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Argentina - Importance of Molecular Imaging Characteristics for the Diagnosis and Management of Tumor-induced Osteomalacia
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v24i1.18
Objective: Tumor-induced osteomalacia (TIO) is a paraneoplastic syndrome associated with the overpro-duction of fibroblast growth factor 23 secondary to phosphaturic mesenchymal tumors (PMT). Our goal was to describe the morphometabolic characterization and histopathological correlation of images obtained from patients with suspected TIO using gallium-68 (68Ga) 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclodo-decane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid (DOTA)-octreotate (68GaDOTATATE) positron emission tomography /computed tomography (PET/CT) in a referral center in Argentina.
Methods: A prospective, descriptive study with patients suspected of TIO who were referred to confirm the presence of primary lesions by 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT.
Results: Eighteen patients were included (female: 72.22%; median age: 47.5 years [range: 41.5–54]). The median maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) was 17.2 (interquartile range: 6.27–30.6). Lesions diagnosed by 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT were predominantly localized in the appendicular skeleton. Most patients had one identifiable lesion. Lesions were focal and well-limited in 66.67% of cases. Histopathological data were available for 13 patients. PMT was diagnosed in 61.54% of cases; in this subgroup, 25% had lesions showing ill-defined borders and confirmed bone erosion. A numerically, non-significant higher SUVmax was found in patients with PMT. Also, a trend towards isolated soft tissue involvement was more commonly observed among these patients.
Conclusion: In our patients with suspected TIO evaluated by 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT, a greater number of lesions were unique, well-defined, and localized in the appendicular skeleton. Nevertheless, ill-defined borders, including bone erosion, were reported in 25% of patients with confirmed PMTs. 68GaDOTATATE PET/CT is a valuable diagnostic tool for patients with suspected TIO. Further research is warranted.--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Morocco - Contribution of [18F] FDG PET/CT in the Diagnosis of Prosthetic Valve Infective Endocarditis
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v24i1.20
Introduction: Infective endocarditis is a potentially life-threatening disease that requires rapid and accurate diagnosis. Recently, [18F] FDG PET/CT has been incorporated as a new major criterion for the diagnosis of infective endocarditis.
Case report: This report describes a 54-year-old female patient who underwent mitral valve replacement in 2018 for symptomatic severe mitral stenosis with atrial fibrillation. She presented with infectious symptoms on clinical examination. Following transthoracic and transesophageal echocardiography, the differential diagnosis included prosthetic valve infective endocarditis versus mechanical prosthesis thrombosis. [18F] FDG PET/CT ultimately confirmed the diagnosis of prosthetic valve infective endocarditis.
Conclusion: This case highlights the significant advantages of [18F] FDG PET/CT in the diagnostic evaluation of patients with suspected prosthetic valve infective endocarditis, particularly when conventional echocardiographic examinations are inconclusive. -

PET/CT of the Breast & Malignant Yolk Sac Tumor of the Ovary in a Child & Cryptic Septic Endocarditis and Systemic Thromboembolism Triggered by Oral Microflora & Contribution of Hybrid SPECT CT Imaging with [99mTc] Tc-MDP in Battered Woman Syndrome
Vol. 23 No. 1 (2025)Marked FDG Uptake on PET/CT Corresponding to Low-Grade Ductal Carcinoma In Situ of the Breast: A Case Report - Denmark
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v23i1.14
This case demonstrates that a focal isolated area of increased FDG uptake on PET-CT should not be disregarded, even if no corresponding lesion is identified on second-look ultrasound.
Low-grade DCIS (Van Nuys Grade 1) may show FDG activity on PET-CT despite its subtle nature.------------------------------------------------------------
Malignant Yolk Sac Tumor of the Ovary Presenting as Adnexal Torsion in a Child: A rare Case Report with Review of Literature - United Kingdom & India
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v23i1.18
Introduction: Malignant yolk sac tumor is a rare ovarian neoplasm with peak incidence in young women. Its occurrence in children less than 10 years old is extremely uncommon. In this manuscript we report a rare case of malignant yolk sac tumor presenting with adnexal torsion, emphasizing the role of multimodality imaging in management.
Case Presentation: A 9-year-old female child was brought with the complaints of acute right lower quadrant pain, nausea and vomiting. On examination, the abdomen was tender with guarding. Laboratory investigations revealed leukocytosis, raised inflammatory markers and markedly elevated alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) levels. Ultrasonography revealed a mixed echogenic tumor in the right adnexa with features of adnexal torsion. Cross sectional imaging confirmed the presence of a heterogeneously enhancing tumor in the right adnexa with pelvic and paraaortic lymphadenopathy. Subsequently, the child underwent emergency laparotomy for adnexal detorsion with tumor excision. Postoperative histopatho-logical examination confirmed malignant yolk sac tumor.
Conclusions: This case underscores the rare presentation of ovarian malignant yolk sac tumor as adnexal torsion in a child and the role of multimodality imaging in its management.
------------------------------------------------------------
Cryptic Septic Endocarditis and Systemic Thromboembolism Triggered by Oral Microflora - USA
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v23i1.16
This unique clinical case underscores the pathogenic nature of oral commensal microbial flora such as Streptococcus Anginosis in provoking infective endocarditis of physiologically normal native heart valves despite the absence of priming systemic risk factors. Understanding the triggering events for this pathological transformation of Stroptococcus Anginosus in normal patients is very much necessary. This will allow the clinicians to anticipate this transpiration in the clinical settings and execute appropriate therapeutic measures to minimize the morbidity and mortality.
------------------------------------------------------------
Contribution of Hybrid SPECT CT Imaging with [99mTc] Tc-MDP in Battered Woman Syndrome - Morocco
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v23i1.20
Introduction: Violence against women is a widespread health problem that knows no racial or social boundaries. It is generally difficult for forensic investigators to obtain medical evidence of violence, particularly in cases where the victims are assessed several months after the event. Bone scintigraphy can be used to identify and document trauma related to acts of torture, and it can also serve as valid evidence in court.
Case report: The bone scan revealed multiple areas of tissue uptake in the early phase, associated with bone uptake in the late phase involving both the axial and peripheral skeleton. In addition, several areas of bone uptake were observed in the late phase without corresponding tissue uptake in the early phase. The scintigraphic pattern demonstrated that the patient's bone lesions were of different ages. Based on these findings, early tissue uptake associated with late bone uptake was consistent with recent post-traumatic lesions, whereas late bone uptake without early tissue uptake was consistent with old post-traumatic lesions. The distribution of certain skeletal lesions suggested a defensive posture adopted by the victim.
Conclusion: In the context of a forensic investigation, bone scintigraphy is a valuable tool that not only detects bone lesions in patients suspected of physical assault, whether or not they present clinical signs, but also helps to determine when the injury occurred.
-
Transient Headache as a Complication of Bronchial Artery Embolization & Unilateral Pulmonary Aplasia & The Ciliated Hepatic Foregut Cyst: A Case-Report and Literature Review
Vol. 22 No. 1 (2025)Original Research:
Transient Headache as a Complication of Bronchial Artery Embolization for Hemoptysis
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v22i1.16
Background: Bronchial artery embolization (BAE) is an established treatment for hemoptysis. While major complications are well documented, transient headaches during the procedure are rarely reported.
Purpose: To determine the frequency, characteristics, and potential mechanisms of headaches occurring during BAE.
Methods: Twenty-six patients (17 male, 9 female; mean age 62.3 ± 13.5 years) undergoing BAE for hemoptysis were prospectively evaluated. All procedures were performed under conscious sedation, using superselective catheterization and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) particles. Headache onset, duration, location, and relation to procedural stage were recorded. Neurological examination was performed immediately post-procedure. Statistical analysis used Fisher’s exact test.
Results: Headache occurred in 17 patients (65.3%). Most episodes arose during PVA injection (76.5%, p < 0.01) and were unilateral in 58.8%, corresponding to the treated side (p < 0.05). All headaches resolved spontaneously after embolization stopped. No patient required analgesics, and no neurological deficits were detected. Headache incidence was unrelated to gender, number of arteries embolized, or underlying cause of hemoptysis.
Conclusion: Transient headache is a relatively frequent and benign event during BAE, often associated with PVA injection and lateralizing to the embolized side. Awareness of this phenomenon allows better patient counselling and procedural reassurance.
Case Report:
The Unilateral Pulmonary Aplasia: Radiologic Clues to a Congenital Anomaly
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v22i1.14
Pulmonary aplasia is a rare congenital developmental malformation characterized by total absence of lung with rudimentary bronchus. Although the exact cause is not known, several factors have been proposed. Patients can be asymptomatic or can present with recurrent respiratory infections. Multimodality imaging may be needed for confirmation and needs to be differentiated from pulmonary agenesis or severe hypoplasia. This case highlights the key imaging findings of pulmonary aplasia and the need for early diagnosis so as to prevent further complications.
Case Report:
Ciliated Hepatic Foregut Cyst: A Case-Report and Literature Review
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v22i1.18
The ciliated hepatic foregut cyst (CHFC) is a rare benign cystic lesion of the liver. Since its initial description fewer than one hundred cases have been reported in the literature. CHFCs are usually asymptomatic and often discovered incidentally during imaging for other reasons. They are most often located in the anterior subcapsular region of segment IV of the liver. The definitive diagnosis is histopathological.
CASE REPORT
We report the case of a 60-year-old man with no significant medical or surgical history who underwent a thoraco-abdomino-pelvic CT scan as part of the workup for a pathological fracture of the left femur. It revealed an oval, well-circumscribed cystic lesion in the anterior subcapsular region of segment IVa. US and MRI were used for further assessment.
DISCUSSION
CHFCs are rare cystic liver lesions resulting from abnormal embryonic development. Although benign, rare cases of malignant transformation have been reported . They typically occur in adults between 50 and 55 years, and a slight male predominance. Most cases are asymptomatic. They are characteristically located in the anterior subcapsular region of segment IV —a key diagnostic clue. Ultrasound, is usually the first-line modality. It reveals a well-defined unilocular cyst with dependent echogenic sediment. CT typically shows a spontaneously hypodense lesion without post-contrast enhancement. MRI is the gold standard for lesion characterization. It reveals the pathognomonic “smurf’s head” appearance, as seen in our case. Histological confirmation is recommended. Management remains controversial as CHFC is not purely benign due to its malignant transformation potential.
CONCLUSION
CHFC is a rare benign liver lesion that should be considered in any middle-aged adult presenting with a unilocular cystic lesion in segment IV. -

TMJ-Arthritis & Anal Fistulas & Display Technology & Paediatric Moya Moya & Sonographic Evaluation of Testicular Volume & Disconcerting Sarcoidosis & Pedal Actinomycetoma
Vol. 21 No. 1 (2025)Septic arthritis of the temporomandibular joint in a 6-year-old boy: A case report
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v21i1.16
Septic arthritis of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is an uncommon condition, particularly in pediatric patients. We present a case of a previously healthy 6-year-old boy who presented with septic arthritis of the TMJ with extra-articular involvement, which responded well to an extended course of intravenous antibiotic therapy, leading to complete resolution on follow-up imaging.
-----------------------------------------------------
Radiology Display Technology: Progress Over Time and the Role of Standards Today
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v21i1.28
Not long ago, X-ray information was recorded on film. Consequently, after development and fixation, post-processing of the image as we use today was simply only possible through another X-ray exposure with additional radiation and uncertain results. The introduction of the digital image information chain from the X-ray detector to the monitor has fundamentally changed this. The digital transformation of radiology has been continuously expanded and improved through the application of new and increasingly powerful technical components. The omnipresence of radiological image information extends from the place of creation via PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System) not only within the radiology department but also throughout the entire hospital and its departments, such as emergency room, operating room, wards, and outpatient clinics of the referring specialties. Further dissemination of digital image information occurs via CD, DVD, USB sticks, and via the internet through patient and referrer portals. The end display devices of the image recipients/users can be projectors, beamers, computer screens, tablets, televisions, smartphones, or other electronic devices with suitable displays. In fact, visualizations of X-ray images on not-too-large displays of car radios are conceivable, for example, if a WhatsApp image message arrives via mobile phone to a radiologist driving a car. Following the desires of the regulatory authorities, all these displays would have to be continuously checked for their display quality because it cannot be ruled out that an X-ray image might be displayed. Theoretically, this is conceivable. However, it is simply not feasible in our overregulated reality by now. Fact-based arguments are discussed regarding this issue, covering various aspects of the diagnostic significance and the technical physical specifications of radiological images. Thus, we provide lawmakers and authorities with evidence-based facts to ensure that future legislative measures appropriately regulate radiologic display quality.
-----------------------------------------------------
A Must-Know Guide to Complex Anal Fistulas Supralevator, Extrasphincteric, and More
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v21i1.14
Treatment of perianal fistulae, especially high-grade Grade 5 perianal fistula, is still a difficult procedure in colorectal surgery. Imaging is central to the correct classification, diagnosis, and preoperative evaluation of fistulae. The purpose of this article is to briefly present the five types of perianal fistula with Grade 5 complexity according to the radiological aspects, classification, and therapeutic implications.
-----------------------------------------------------
Unravelling paediatric stroke: a rare presentation of paediatric Moya moya disease with simultaneous involvement of anterior and posterior circulation https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v21i1.20Moya Moya disease is a rare cerebrovascular disorder characterized by progressive stenosis of the internal carotid arteries and their branches, leading to a range of neurological symptoms. This case report discusses a 14-year-old boy presenting with classic symptoms associated with Moya Moya disease. The diagnostic process involved imaging studies, which confirmed the characteristic findings of the disease along with a specific ANA study which further helped in excluding the association of any other autoimmune disease. Treatment options were explored, including, the use of therapeutic drugs like Aspirin and some statins, aimed at preventing TIAs and alleviating symptoms. This case highlights the importance of early recognition and management of Moya Moya disease to prevent serious neurological deficits and improve the quality of life in affected children and adolescents. Further research is needed to explore the long-term outcomes of various treatment strategies for this challenging condition.
-----------------------------------------------------
Sonographic Evaluation of Male Testicular Volume Amongst Patients With Fertility Challenges: A Cross-Sectional Retrospective Study
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v21i1.18
Background
Male infertility is a significant health issue affecting approximately 15% of couples worldwide. Testicular volume has been suggested as a potential predictor of fertility issues in men, but no study has correlated testicular volume amongst men with infertility challenges in our environment. The purpose of the study is to evaluate the relationship between testicular volume and male fertility profile in subjects with fertility challenges.
Methods
The research involves a cross-sectional retrospective analysis of records of male patients that presented to the teaching hospital with fertility concerns. Records containing age, Ultrasound measurement of testicular volume, sperm count, and sperm motility were taken into account. Sample size used was 50 records of male patients that presented with infertility. Independent samples t-test and Pearson correlation were employed at a 5% level of significance.
Results
Our results suggest that patients with lower testicular volume may have compromised sperm production and quality, thus contributing to infertility. There was a significant difference between the testicular volume of infertile males and fertile males [RT. Volume (p = <0.0001) & LT. Volume (p < 0.0001)]. Findings in correlating testicular volume with sperm parameters shows there was a significant relationship between sperm motility sluggish and left testicular volume (r = 0.301, p = 0.034) and between sperm count and left testicular volume (r = 0.317, p = 0.025). For sperm motility activeness (r = 0.092, p = 0.532) and sperm motility deadness (r = 0.031, p = 0.828), there was no significant relationship.
Discussion
The result from the analysis showed there was a positive significant difference in the values of the testicular volumes of infertile and fertile male patients with the testicular volume for infertile males lesser than the normative volume for fertile males.
Conclusion
This study showed that the mean testicular volume in male with fertility challenges are lesser. Smaller testicular volume was associated more with lesser sperm motility sluggishness and reduced sperm count. This implies that clinicians could include testicular volume measurements as part of routine fertility assessments to help identify individuals at risk for infertility.
-----------------------------------------------------
A disconcerting sarcoidosis, when the spine gets involved...
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v21i1.22
Bone involvement in sarcoidosis is uncommon and may be discovered incidentally when pain appears in affected patients. Indeed, the pelvic-spinal location is the most widespread: It can manifest when the spine is affected by inflammatory pain, sometimes mimicking authentic spondyloarthritis in certain cases, and may even suggest a malignant lesion by its radiological appearance. We describe the original observation of a patient suffering from inflammatory and insomnia-causing spinal pain in whom the diagnosis of mediastinal sarcoidosis was retained in therapeutic abstention on the pulmonary level.
Observation: 52-year-old female patient who had presented for barely a year a chronic cough accom-panied by basithoracic pain, leading her to perform a chest CT scan which found bilateral mediastinal-hilar adenopathies and peri-lymphatic pulmonary nodules. The diagnosis of type 2 sarcoidosis was immediately considered. The additional investigations have indeed confirmed the suspected disease on the clinical and radiological level, in particular by converse enzyme positivity, the tuberculin anergy on the IDR, the lymphocyte predominance in the bronchoalveolar fluid but more particularly by the demonstration of the epithelial-giant cellular granuloma on the right iliac lymph node biopsy. However, the patient presents with intense inflammatory back pain, sometimes causing insomnia. A spinal MRI showed no-dular bone marrow replacement lesions with pronounced T1 hyposignal and T2 hypersignal enhanced after gadolinium injection. Fortunately, she does not present bone fractures and no osteoporosis on bone densitometry.
Conclusion: Faced with spinal symptoms in a context of sarcoidosis, bone involvement must be considered, especially since there is no correlation between the clinical picture and imaging. The latter most often has a favorable prognosis in the absence of fractures despite sometimes suspicious imaging. The case of our patient clearly illustrates the bone-related nature of the disease; back pain can be particularly intense and should lead to discussion of the use of corticosteroids or even basic treatment for rheumatic diseases.
-----------------------------------------------------
A Radiologist's view on Pedal Actinomycetoma: A Case Report with Comprehensive Review of Literature
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v21i1.26
Background: Tropical diseases comprise of an array of communicable and non-communicable diseases that prevail in the tropical belt. Madura foot, classified as a tropical disease by WHO, is a chronic granulomatous disease that predominantly involves the skin and subcutaneous tissue, commonly affecting the lower limbs. We present a case of actinomycetoma with extensive review of the existing literature, focusing on diagnostic imaging.
Case presentation: A 36-year-old female from eastern India presented with a six-month history of right foot swelling and a discharging wound. She was unsuccessfully treated with multiple courses of antibiotics in local hospitals. Upon referral, radiological investigations were performed for further evaluation. USG showed infiltrative hypoechoic soft tissue with nodular lesions showing targetoid appearance. MRI revealed infiltrative soft tissue with variable sized nodular lesion showing characteristic ‘dot-in-circle' appearance, prompting the diagnosis of pedal mycetoma. Actinomycetoma was confirmed on biopsy.
Conclusion: Pedal mycetoma presents significant diagnostic and therapeutic challenges owing to its insidious progression and delayed diagnosis. Radiological imaging, particularly MRI, plays a pivotal role in diagnosis and staging of the disease, enabling detailed evaluation of soft tissue and bone involvement. The ‘dot-in-circle' sign observed on imaging is pathognomic and aids in accurate diagnosis. Early dia-gnosis facilitated by diagnostic imaging warrants improved therapeutic outcomes.
-
Prostate Sarcoma, Famous Poisonings, Cardiac MRI
Vol. 20 No. 1 (2025)Case Report:
Prostatic Sarcoma
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v20i1.16
(from Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, University Medicine Oldenburg, Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg, Oldenburg, Germany)
Prostatic sarcomas are rare and aggressive malignancies, often presenting with nonspecific symptoms that mimic benign urological conditions, potentially leading to diagnostic delays [1]. This case outlines the clinical course of a 42-year-old male with a prostatic sarcoma, emphasizing the importance of early imaging, histopathological assessment, and multidisciplinary oncological management.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Special Area - Highlights from related disciplines:
Pharmacology & Toxicology - Famous Poisonings in History
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v20i1.14
(from Royal Academies of Medicine and Related Sciences of Murcia and Valencia, Spain)
The use of poisons spans human history, serving as tools for war, execution, assassination, revenge, and political control. Ancient texts like the "Rig Veda" mention poisoned weapons, and many civilizations used natural toxins—such as frog skin, snake venom, and plant extracts—for lethal purposes. Mythology reflects deep knowledge of poisons. Medea attempted to poison Theseus with aconite to protect her son’s claim to the throne. Hercules used Hydra’s venom to create deadly arrows. In historical contexts, figures like Socrates were executed with poison—hemlock in his case—which was reserved for elite criminals due to its cost. Classical toxicology began in Ancient Greece and continued through the Roman Empire. During Rome’s imperial era, poisons were commonly used in power struggles. Tiberius’ reign saw suspected poisonings of his potential successors, including Germanicus and Drusus. Caligula ultimately rose to power through such intrigue, killing his rivals. Notable toxicologists include Mateo Orfila, who advanced forensic detection techniques in the 19th century, and Juan Bautista Peset Aleixandre, who developed early devices to detect toxic gases in the blood. Natural poisons were also studied in modern science. Cobra venom contains dozens of toxic proteins, many of which disrupt nerve and muscle function. Aconitine, found in "Aconitum napellus", binds to sodium channels in nerves, keeping them open and causing fatal disruptions in cell signaling. Another plant-based toxin, protoanemonin from buttercups, causes painful spasms and ulcers, giving rise to the term "sardonic smile". In Renaissance and Baroque Europe, poisoners like Locusta in Nero’s Rome and La Voisin in Louis XV’s court gained notoriety for their lethal skills. They supplied aristocrats with toxic mixtures to remove rivals or secure inheritances. One infamous potion, “Aqua Tofana”, was linked to hundreds of deaths, possibly including that of Mozart. Venice’s secretive Council of Ten used poison for state security, relying on anonymous citizen reports and aconite-based poisons. In France, women like the Marquise de Brinvilliers and La Voisin were executed for mass poisonings. These individuals often disguised their poisons as medicine or spiritual remedies, exploiting trust and social status. Through myth, science, and scandal, poisons have left an indelible mark on human history, both as instruments of death and as subjects of fascination and fear.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Original Research:
MRi Regional Strain Analysis in Patients with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v20i1.18
(from Bristol Heart Institute, University Hospitals Bristol and Weston NHS Foundation Trust 2025, Bristol, United Kingdom)
Purpose: To evaluate the regional left ventricular myocardial strain in patient with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) especially young apparently compensated patients by magnetic resonance imaging.
Materials and Methods: 25 HCM patients representing all age groups and 25 healthy volunteers underwent 1.5 Tesla MRI examination for cardiac volumes, and mass, followed by regional strain analysis in radial, circumferential, and longitudinal directions as regard the displacement, strain, peak diastolic and systolic strain rate, peak diastolic and systolic velocity, time to peak displacement and time to peak strain.
Results: In the HCM group, hypertrophic segments showing delayed gadolinium enhancement (DGE) were significantly different from non-hypertrophic apparently normal showing no enhancement concerning most of the regional radial strain parameters.
In longitudinal and circumferential directions, hypertrophic segments showing DGE were significantly different from apparently normal segments with no enhancement as regard the strain, peak diastolic and systolic strain rate. Compared to normal volunteers, the hypertrophic segments with DGE were significantly different concerning most of the radial and longitudinal strain parameters, while apparently normal segments with no enhancement don’t present a similar significant difference.
In circumferential analysis, hypertrophic enhancing segments were significantly different as regard the strain, peak diastolic strain rate, peak systolic velocity, and time to peak displacement, while the apparently normal non-enhancing segments present difference concerning the strain, peak systolic velocity, and time to peak displacement.
Conclusion: The hypertrophied segments are more affected than the segments of apparently normal thickness in HCM patients, especially in the radial direction, the apparently normal segments are also affected with no tendency of functional compensation. Our data show that HCM muscle fibers show mostly hypofunction and reduced contraction rather than hypercontraction and even the apparently normal segments are impaired to a certain degree in comparison to normal. These findings are essential in follow up studies especially with patient receiving myosin inhibitors as well as young patients presenting preserved cardiac function and for gene positive apparently normal with absent penetration of the gene in the form of a concentric thickening can be seen by imaging, do we need more sophisticated imaging process like strain analysis to ensure absent penetration.
-
May 2025 - Vol. 19 - Swiss Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine
Vol. 19 No. 1 (2025)Radiologically Equivocal Bone Lesions Finally Diagnosed by Bone Scan
Bone scintigraphy remains the second highest volume procedure in nuclear medicine laboratories with diverse applications. Bone scans are highly sensitive and can detect abnormalities much earlier than conventional X-rays. They provide a full-body image, allowing for the assessment of multiple bone sites simultaneously. they can also show specific patterns associated with specific diseases, eliminating ambiguity in diagnosis and establishing a specific diagnosis. Bone scan may be the final station to confirm the diagnosis of certain bone lesions that appear equivocal on other imaging modalities. There are some conditions where bone scans can be considered accurate and guide precise diagnosis, particularly when interpreted in conjunction with clinical findings and/or other imaging modalities as bone metastases, myositis ossificans, osteomyelitis, discitis, avascular necrosis, metabolic bone disease, fibrous dysplasia, osteopetrosis, stress fractures, Rheumatoid arthritis, reflex sympathetic dystrophy, transient migratory osteoporosis, hypertrophic osteoarthropathy, osteoid osteoma, condylar hyperplasia and osteopoikilosis.
-

April 2025 - Vol. 1 - Swiss Journal of Radiology and Nuclear medicine
Vol. 18 No. 1 (2025)Original Research:
Supporting Radiologists with Automated Image Analysis: An Evaluation of Deep Learning Tools for Augmenting Breast Cancer Screening
Case Reports:
1) Cerebral hyperperfusion syndrome following carotid endarterectomy
2) Ovarian Dermoid Cyst Invading Into Urinary Bladder
-

Manners maketh man
Vol. 16 No. 1 (2025)"Manners maketh man." This quote from William of Wykeham (1324–1404) conveys the idea that good manners and education are fundamental in shaping a true human being. Throughout history, societies have been considered civilized once they developed the ability to write. So, when are you ready to start writing?
-

Metastatic Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor & A Rare Case of Asymptomatic Aortocaval Fistula Discovered During Routine Imaging
Vol. 15 No. 1 (2025)Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors (MPNST) are rare and aggressive soft tissue sarcomas arising from the peripheral nerves. These tumors are associated with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), and though they can occur sporadically, their diagnosis can be complex, especially when metastases are present. This case describes a young female patient with MPNST located in the dorsolumbar region and metastatic spread to the lungs, along with a history of acoustic neuroma.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Aortocaval fistulas resulting from abdominal aortic aneurysms are rare, representing 3–6% of ruptured cases. These fistulas are often asymptomatic or present with non-specific symptoms related to venous hypertension or high-output cardiac failure. Fortuitous diagnoses in asymptomatic patients are exceedingly uncommon.
Case Presentation:
An 86-year-old woman underwent CT angiography to evaluate left leg circulatory issues. Imaging revealed an aortic aneurysm with a fistula into the inferior vena cava, an enlarged right atrium, and pelvic vein varices. The asymptomatic fistula was treated with endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR). Postoperatively, the patient developed superior mesenteric artery occlusion and intestinal ischemia, leading to palliative care and death.
Discussion:
Aortocaval fistulas can result from a variety of causes including infection and trauma. Diagnosis is typically achieved through CT angiography. While open surgical repair remains the standard treatment, EVAR is a viable alternative in selected cases. However, the prognosis remains guarded, even with appropriate treatment.
Conclusion:
Aortocaval fistulas are rare and life-threatening conditions that require prompt diagnosis and management, though outcomes are often poor.
-

December - Happy Holidays from Switzerland and a Happy New Year 2025!
Vol. 14 No. 1 (2024)Switzerland, December 2024,

Charting the Evolution of Medical Publishing and State of the Swiss Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine after 18 Months of Impact - Editorial Communication
As we celebrate 18 months since the launch of the Swiss Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine (www.SJORANM.com), it is both a privilege and an inspiration to reflect on the journey that has brought us to this significant milestone. Since its establishment in June 2023, the journal has rapidly grown into a dynamic platform that bridges disciplines, fosters innovation, and contributes to the global dialogue in radiology and nuclear medicine. Our presence extends beyond traditional boundaries, leveraging the reach of social media platforms such as YouTube, LinkedIn, X, TruthSocial, Facebook, Instagram, TikTok, and others. The rapidly growing number of followers on these channels underscores their potential as transformative tools for scientific communication. Unlike conventional publishing formats, these platforms enable the dissemination of scientific content not only through text but also via audio and video, offering unprecedented opportunities to engage and educate diverse audiences. This evolution mirrors other technological disruptions. Just as email rendered fax and postal mail obsolete within months of its inception, scientific publishing is poised for a similar transformation. The advent of low-cost, high-impact tools for creating and sharing content challenges the traditional publishing models, compelling established publishers to adapt or risk obsolescence. As we continue this journey, we remain committed to embracing innovation and fostering a collaborative, forward-thinking approach that ensures the Swiss Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine remains at the forefront of scientific communication.
-------------------------------------------------------
Original Article from Vascular Solutions of North Carolina, USA - Case Series Analysis of Trans-Arterial Embolization for Osteoarthritis-Related Hand Pain
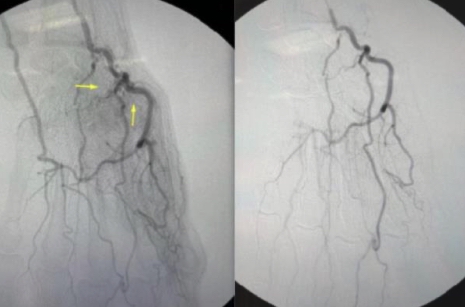
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a widespread disorder which commonly impacts a significant portion of the population. Although most cases involve the knee joint, it can also affect the carpometacarpal joint and cause significant pain in the hand and thumb. Traditional treatments often provide short-term pain relief and need continual treatment prompting the need for exploring alternative therapies to prolong the duration of pain relief. This case series assesses the clinical success of trans-arterial embolization (TAE) of the joints in the hand as a minimally invasive treatment for chronic pain associated with hand joint OA, defined as a 50% (or greater) decrease in Visual Analog Scale (VAS) score overall, as well as a decrease in prescribed pain medication use. We present a case report of four patients who underwent this intervention for hand joint osteoarthritis. Preliminary results show an average decrease in VAS exceeding the 50% threshold, with a notable reduction in pain medication usage and improvements in daily activities. These findings suggest that TAE shows promise as a minimally invasive therapy for hand joint OA, warranting further investigation into its long-term efficacy and safety.
-
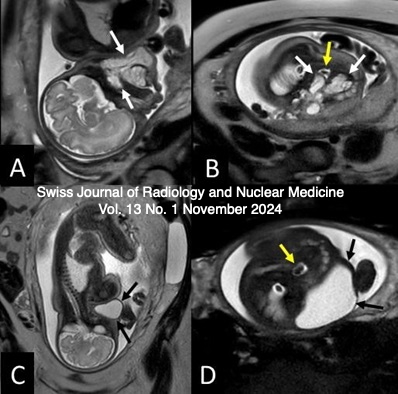
Lymphatic Malformations & Navigating Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Connections & Denosumab-Induced ONJ
Vol. 13 No. 1 (2024)Lymphatic Malformations
Vascular anomalies correspond to a group of lesions related to disorders of vascular develop- ment, which to date remain a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge for treating physicians. Lymphatic malformations (LM) are congenital malformations that manifest as benign hamartomatous tumors of the lymphatic vessels with a marked predilection for the head, neck and oral cavity. In general terms, LM are classified as macrocystic, microcystic or a combination of both depending on the size of the lesion, which can lead to anatomical alterations and even functional deficits. The aim of this article is to provide a brief and accurate review of head and neck lymphatic malformations considering their clinical aspects, imaging tools and treatment options.
-------------------------
Navigating complexity: A pictorial representation of anomalous pulmonary venous connection classification in the pediatric population with volume rendering and multiplanar imaging technique
Anomalous pulmonary venous connections represent a heterogeneous group of congenital heart diseases in which a part or all of the pulmonary veins drains into the right atrium instead of draining into the left atrium. Pulmonary venous anomalies can manifest as partial or total anomalous drainage due to the abnormal embryological development. Multidetector CT angiography, with its multiplanar reformatting and volume rendering techniques, precisely offers the information about the three-dimensional anatomy and spatial relationships of the cardiovascular structures. Clinical features of anomalous pulmonary venous connections may be silent or have variable features like neonatal cyanosis, volume overload, and pulmonary arterial hypertension due to the left-to-right shunt, which are often associated with other congenital cardiac disease, so that accurate diagnosis is essential for treatment planning.
-------------------------
Denosumab-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Jaw with FDG PET/CT Imaging Features
Denosumab is a monoclonal antibody that inhibits receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand (RANKL), which plays a crucial role in osteoclast formation, function, and survival. By blocking RANKL, denosumab helps prevent bone resorption, making it an effective therapeutic option for managing conditions associated with bone metastases and osteopenia, such as in patients with lung cancer. Lung cancer, particularly non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), often metastasizes to bones, and denosumab is commonly used to reduce the incidence of skeletal-related events (SREs) in these patients. However, denosumab therapy is not without its risks, and one of the most significant side effects is osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ), a potentially debilitating condition characterized by bone exposure and necrosis, typically following dental extractions or trauma
-
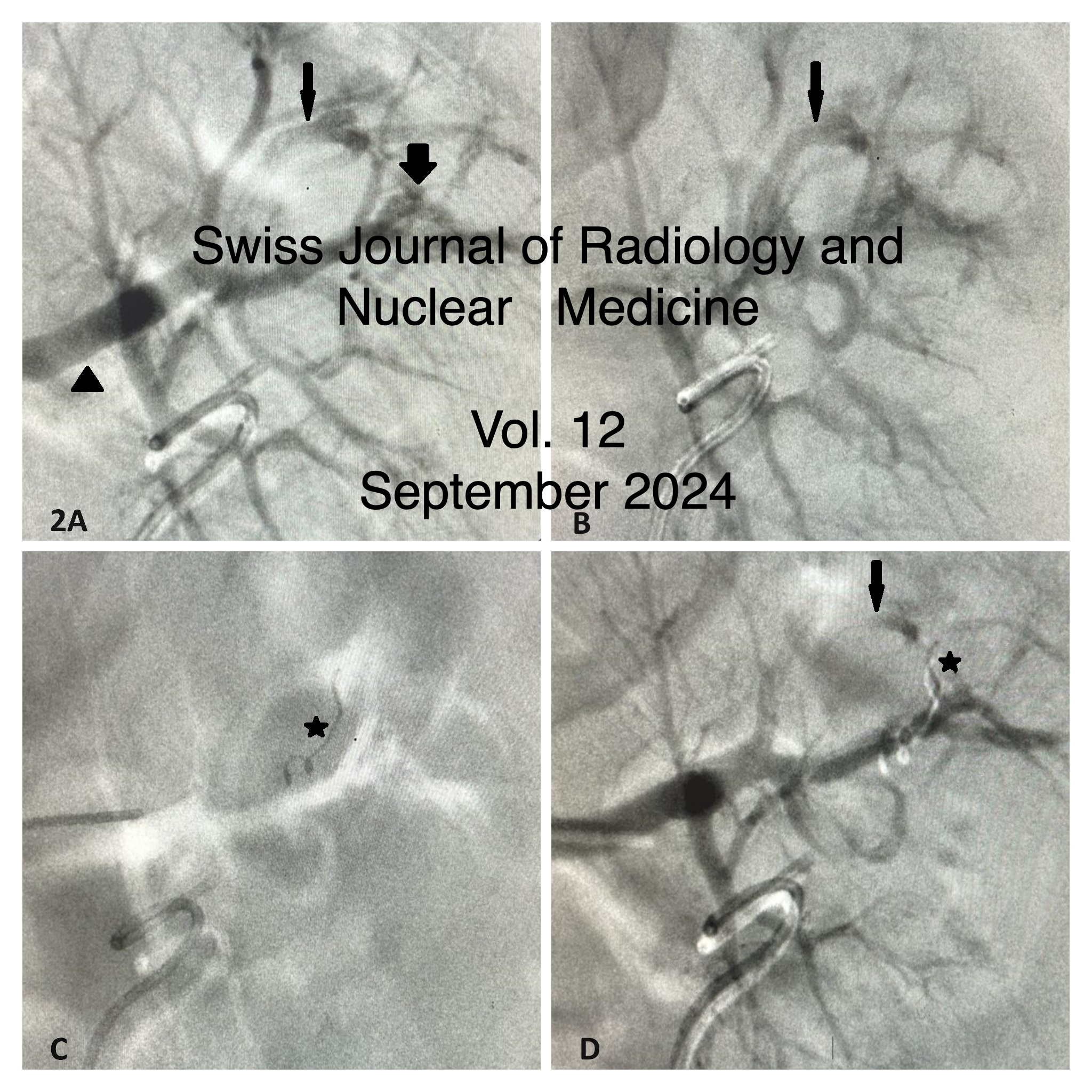
Synchronous endovascular management of post PCNL concurrent pseudoaneurysm and AV fistula & Automatic Joint Teeth Segmentation in Panoramic Dental Images using Mask Recurrent Convolutional Neural Networks with Residual Feature Extraction: Can it be useful in Oral Cancer Diagnosis and Management?
Vol. 12 No. 1 (2024)Synchronous endovascular management of post PCNL concurrent pseudoaneurysm and AV fistula
Percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL) is the standard treatment procedure for large stones associated with complications like pseudoaneurysm and arteriovenous fistula with their incidence being < 1%. A post-PCNL case with left flank pain and delayed haematuria presented with macroscopic haematuria and depleting haemoglobin levels. CT angiography with 3-D reconstruction was used for diagnosing and planning of treatment. The patient was successfully treated with super selective angioembolization (SAE) using peripheral coils while preserving the kidney's remaining vascularization. Early diagnosis and active endovascular treatment using angioembolization techniques can be life-saving and resulting in minimal post-procedure complications and early recovery.
Automatic Joint Teeth Segmentation in Panoramic Dental Images using Mask Recurrent Convolutional Neural Networks with Residual Feature Extraction: Can it be useful in Oral Cancer Diagnosis and Management?
Introduction: Panoramic dental images gives an in-depth understanding of the tooth structure, both lower and upper jaws, and surrounding structures throughout the cavity in our mouth. The Panoramic dental images provided have significance for dental diagnostics since they aid in the detection of an array of dental disorders, including oral cancer. We propose a novel approach to automatic joint teeth segmentation using the pioneer Mask Recurrent Convolutional Neural Network (MRCNN) model for dental image segmentation.
Material and Methods: In this study, a sequence of residual blocks are used to construct a 62-layer feature extraction network in lieu of ResNet50/101 in MRCNN. To evaluate the efficacy of our method, the UFBA-UESC and Tufts dental image dataset (2500 panoramic dental x-rays) were utilised. 252 x-rays were used in test set, rest of the x-rays were utilised as training (1800 images) and validation datasets (448 images) in ratio of 8:2 of the modified MRCNN model.
Results: Modified MRCNN achieved the final training and validation accuracies as 99.67% and 98.94%, respectively. The achieved accuracy of Dice coefficient (97.8%), Intersection over Union, (98.67%), and Pixel Accuracy (96.53%) respectively over the whole dataset. We also compare the performance of proposed model and other well established networks such as FPN, UNet, PSPNet, and DeepLabV3. The Modified MRCNN provides better results segmenting any two teeth which are close to each other.
Conclusion: Our proposed method will serve as a valuable tool for automatic segmentation of individual teeth for medical management. This current method leads to higher accuracy and precision. Segmented images can be used to evaluate periodic changes, providing valuable data for assessing the progression of oral cancer and the efficacy of management. Future research should focus on developing less complex, lightweight, and faster vision models while maintaining high accuracy
-
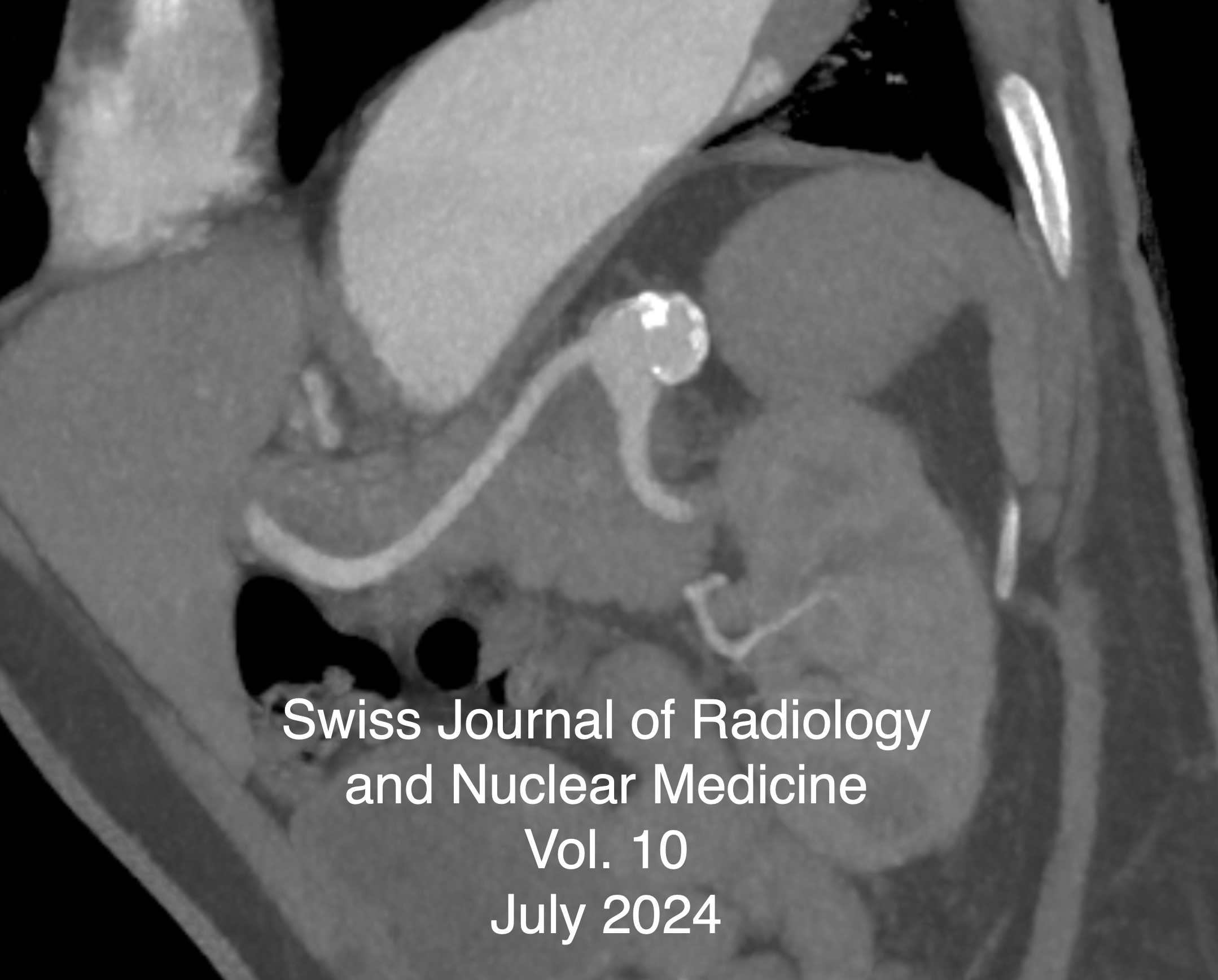
Splenic Artery Aneurysm Occlusion & Nasopharyngeal Metastasis of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma & Study of Multimodality Imaging Features of Brown Tumor or Osteitis Fibrosa Cystica
Vol. 10 No. 1 (2024)Splenic Artery Aneurysm Occlusion
The first lienal artery aneurysm was discovered and described for the first time in 1770 by the Frenchman Beaussier during an autopsy. It was first visualised using X-rays in 1920 by the physicians Akbulut and Otan. The first surgical treatment of a splenic artery aneurysm was performed by surgeons MacLeod and Maurice in 1940. The first minimally invasive endovascular therapies using coils, stents or a combination of the two devices for minimally invasive treatment of aneurysms of the lienal artery were reported in 1990, 1994 and 1995...
Nasopharyngeal Metastasis of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) despite of an indolent clinical behavior is known to cause locoregional recurrence and distant metastasis. Lung and bone are the common site of distant metastasis. Nasopharynx is a very rare site of metastasis.
Study of Multimodality Imaging Features of Brown Tumor or Osteitis Fibrosa Cystica
Brown tumor, also known as osteitis fibrosa cystica, is a rare but significant manifestation of hyperparathyroidism characterized by focal bone lesions resulting from excessive osteoclastic activity. Despite its rarity, Brown tumor poses diagnostic challenges due to its varied clinical presentations and radiographic features, often mimicking other bone lesions such as giant cell tumors or metastatic disease.
-
Ultrasound Analysis of the Most Important Musculoskeletal Issues
Vol. 9 No. 2 (2024)This issue shows the most important standard sections of relevant questions in musculoskeletal (MSK) ultrasound of the wrist, elbow, shoulder, hip, knee and ankle. Exemplary images with descriptions of the sections and anatomical structures were created and the positioning of the patient explained. Several patient cases per region are being presented and explained in order to place the described procedures in a clinical context. The advantages and disadvantages of the imaging procedures are being explained and compared.
-
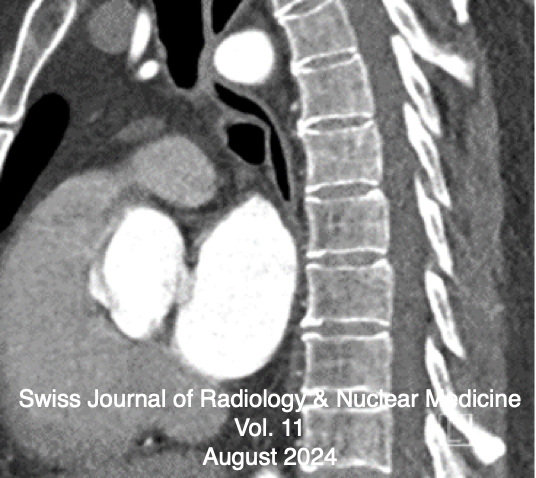
Mediastinal Distortions & Archimedes Leverage of Research Funding
Vol. 11 No. 1 (2024)Learnings from Archimedes on the leverage of medical research funding in the post-Corona era
The Corona pandemic has increased pre-existing financial pressure on universities further. Universities will face closure as a realistic scenario in the future, and need to compete for research success. Medical faculties are at a particular risk of being the subject of cost-cutting measures. In this challenging environment, using the concept of financial leverage is key for maximising financial possibilities.
Mediastinal Distortions: A Rare Case of Congenital Anatomic Relocations of Mediastinal Structures and Vascular Anomalies in Combination with Heterotopic Conduction in Pulmonary Veins and Sick Sinus Syndrome
The case we present involves an atypically developed thoracic aorta, resulting in the consecutive displacement of the trachea and esophagus, combined with the unusual formation of vascular bridges between the ascending and descending thoracic aorta and the arising supraaortic branches. This represents a pathological entity further associated with a cardiac condition of Sick Sinus Syndrome and heterotopy of the excitation center in the pulmonary veins. Multiple descriptions of the combination of dextrocardia and Sick Sinus Syndrome have been reported by Aurora Bakalli et al. 2021 (1), as well as the combination of dextrocardia, persistent left superior vena cava, and Sick Sinus Syndrome by Gangliang Guo et al. 2017 (2), and another case of dextrocardia and Sick Sinus Syndrome by Junqian Luo et al. 2022 (3). Such combinations of anomalies have not been reported in larger statistical collections to date.
-
PRIMARY CHORIOCARCINOMA OF THE VULVA & OTHER SPECIAL CASES
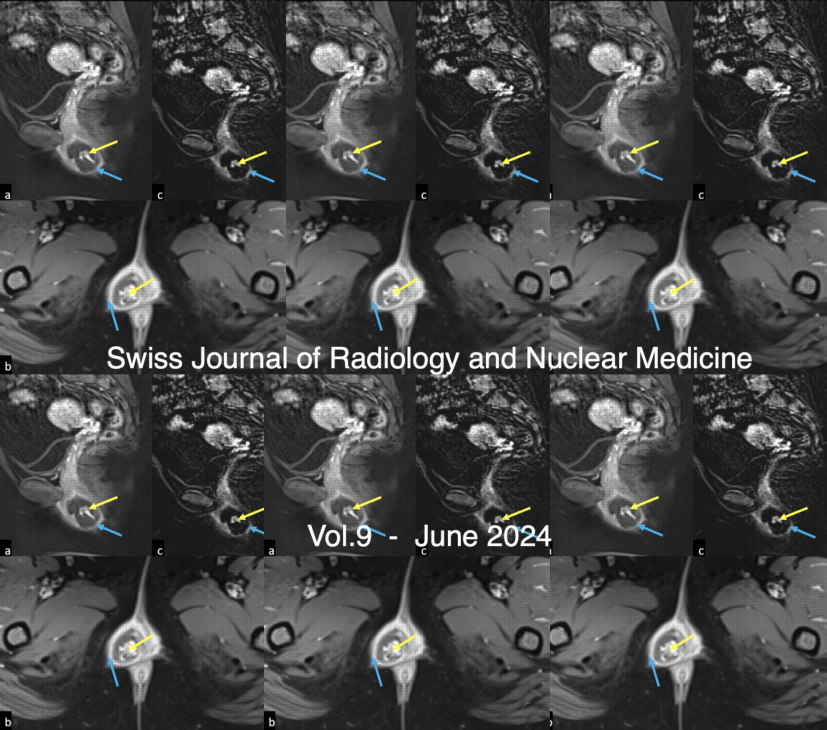
Vol. 9 No. 1 (2024)Gestational choriocarcinoma usually occurs in the corpus uteri in association with a coincident or antecedent pregnancy. Primary extrauterine choriocarcinoma is a rare entity, with the cervix being the most common site. We report a rare case of primary choriocarcinoma of the vulva in a woman with previous partial molar pregnancy and highlight its Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) features. -
Liver disease & Ovarian Goitre
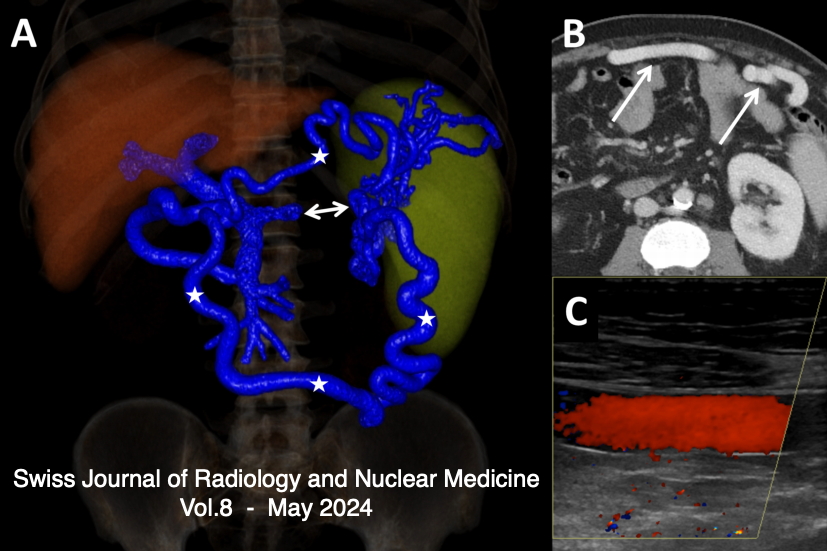
Vol. 8 No. 1 (2024)Splenic vein thrombosis is frequently diagnosed in the chronic stage, when collaterals have already developed. In this case, the presence of two major spontaneous shunts between the splenic vein and the superior mesenteric vein is preventing complications such as porto-systemic encephalopathy and variceal bleeding.
-

AI and ChatGPT help Radiology. Do they?
Vol. 7 No. 2 (2024)Interventional Radiology was, is and will be always busy. Our patients benefit from well planned and skilled performances done by physicians, who are free from bureaucracy. Can AI help? Perhaps it can help, first of all within the field of paperwork and endless documentation...later on perhaps AI will perform pleura drainage or PICC-Line insertion by itself. Time wil show.
-
Issue April 2024
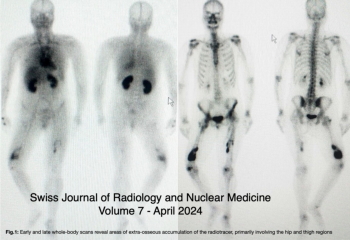
Vol. 7 No. 1 (2024)This work provides an overview of the effectiveness of bone scintigraphy and its role in diagnosing various benign conditions in the Nuclear Medicine Department of the University Hospital of Fez. It analyzes the criteria for selecting scintigraphy as a diagnostic tool and outlines the principles, key features, and protocols involved. These details support clinicians in confirming their diagnostic reasoning when evaluating musculoskeletal lesions or bone abnormalities, guiding their choice of imaging modalities. Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP) is an extremely uncommon autosomal dominant condition marked by abnormalities in the big toes and the gradual development of extra-skeletal bone in specific anatomical formations.
-
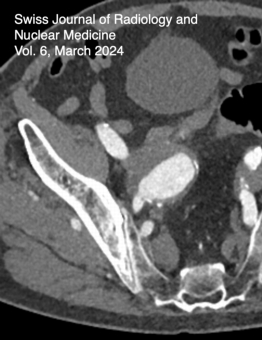
Endovascular Intervention
Vol. 6 No. 1 (2024)In cases where there is insufficient occlusion of the aneurysm with residual perfusion, secondary embolization becomes considerably more complex due to the occlusion of the anatomically antegrade access and the altered hemodynamics around the aneurysm causing retrograde collateralization