Vol. 10 No. 1 (2024): Splenic Artery Aneurysm Occlusion & Nasopharyngeal Metastasis of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma & Study of Multimodality Imaging Features of Brown Tumor or Osteitis Fibrosa Cystica
Splenic Artery Aneurysm Occlusion
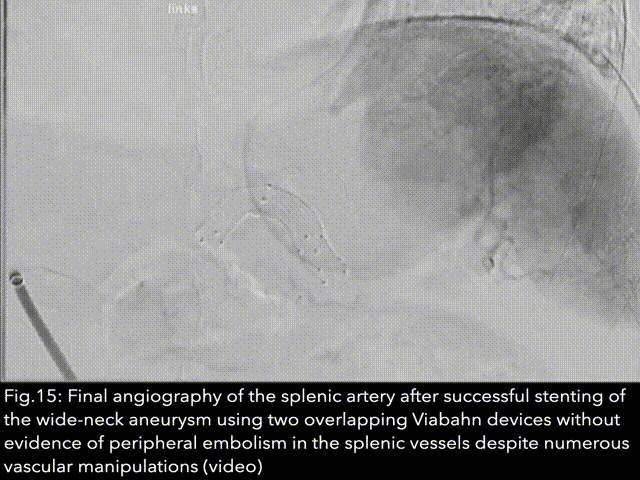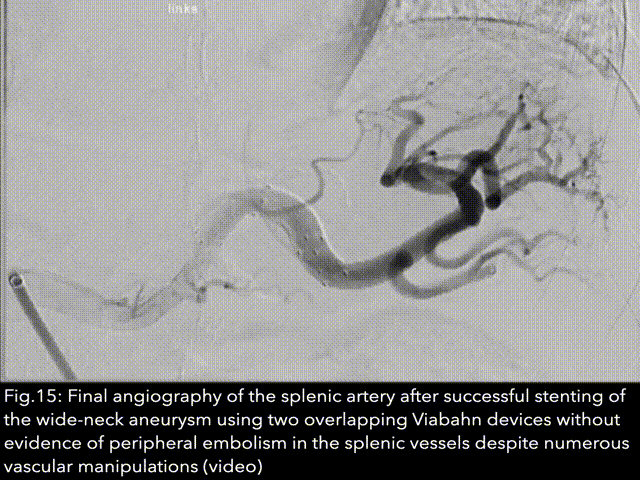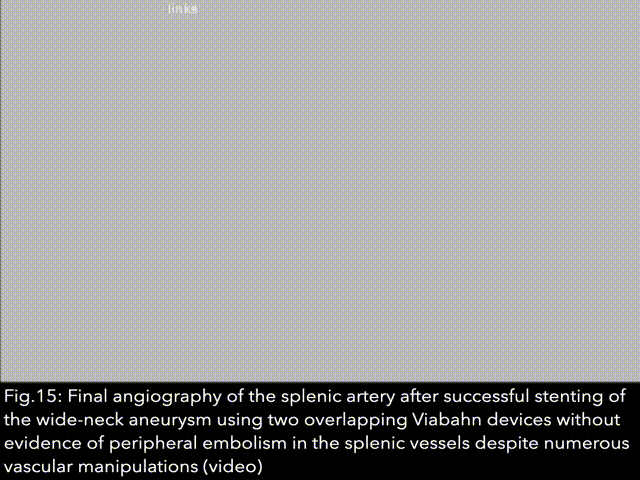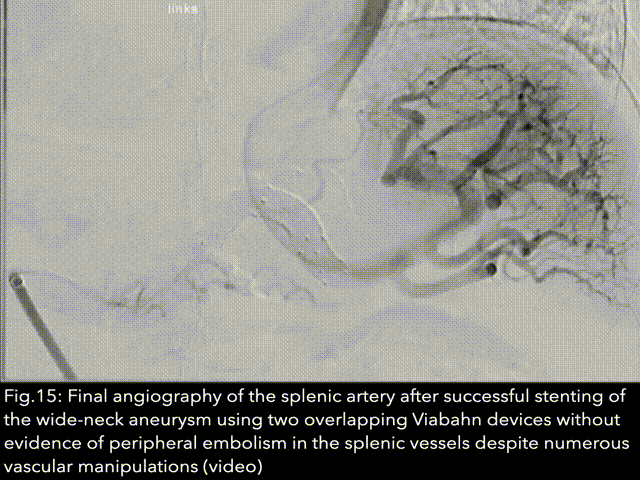
The first lienal artery aneurysm was discovered and described for the first time in 1770 by the Frenchman Beaussier during an autopsy. It was first visualised using X-rays in 1920 by the physicians Akbulut and Otan. The first surgical treatment of a splenic artery aneurysm was performed by surgeons MacLeod and Maurice in 1940. The first minimally invasive endovascular therapies using coils, stents or a combination of the two devices for minimally invasive treatment of aneurysms of the lienal artery were reported in 1990, 1994 and 1995...
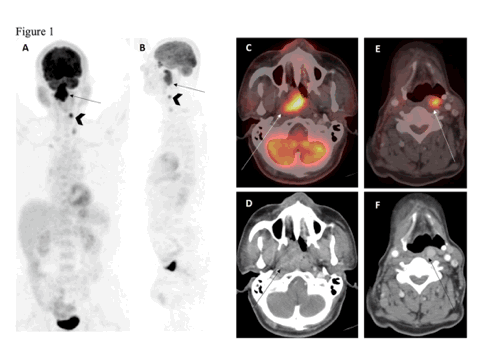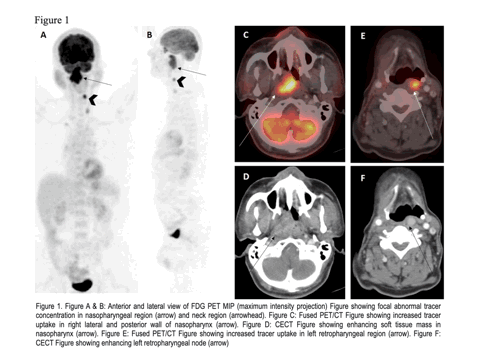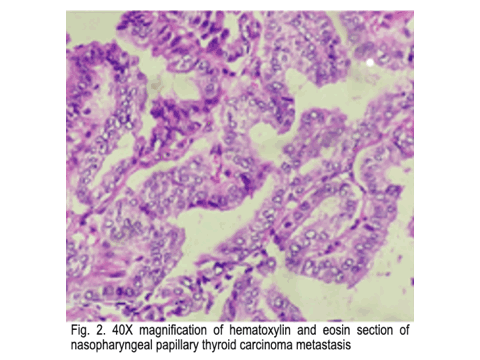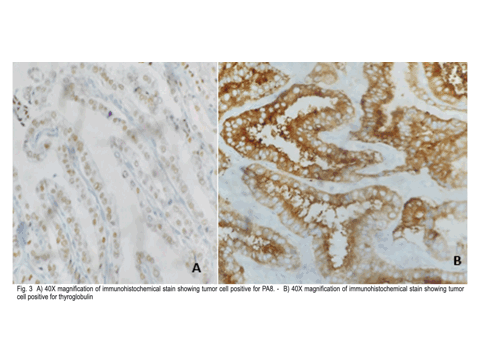
Nasopharyngeal Metastasis of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) despite of an indolent clinical behavior is known to cause locoregional recurrence and distant metastasis. Lung and bone are the common site of distant metastasis. Nasopharynx is a very rare site of metastasis.
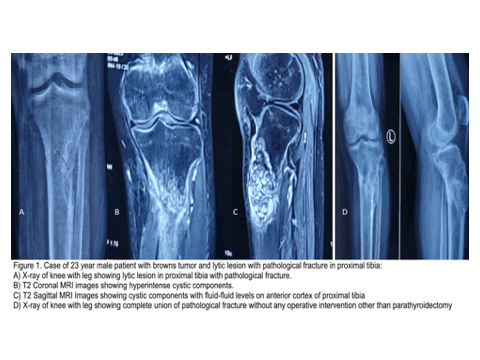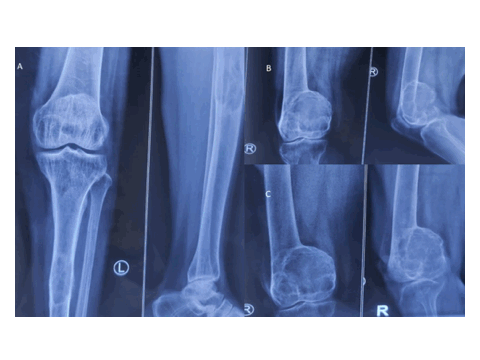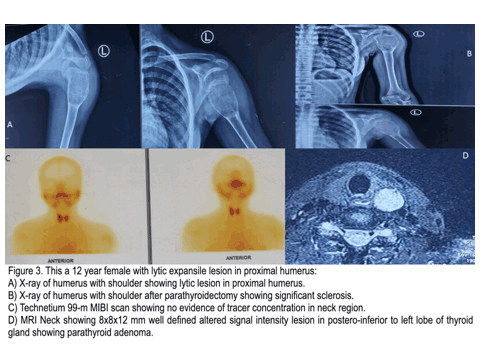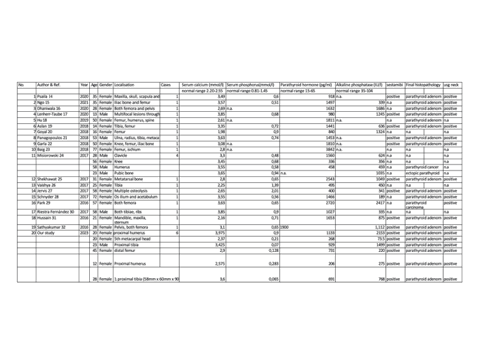
Study of Multimodality Imaging Features of Brown Tumor or Osteitis Fibrosa Cystica
Brown tumor, also known as osteitis fibrosa cystica, is a rare but significant manifestation of hyperparathyroidism characterized by focal bone lesions resulting from excessive osteoclastic activity. Despite its rarity, Brown tumor poses diagnostic challenges due to its varied clinical presentations and radiographic features, often mimicking other bone lesions such as giant cell tumors or metastatic disease.