Vol. 23 No. 1 (2025): PET/CT of the Breast & Malignant Yolk Sac Tumor of the Ovary in a Child & Cryptic Septic Endocarditis and Systemic Thromboembolism Triggered by Oral Microflora & Contribution of Hybrid SPECT CT Imaging with [99mTc] Tc-MDP in Battered Woman Syndrome
![View Vol. 23 No. 1 (2025): PET/CT of the Breast & Malignant Yolk Sac Tumor of the Ovary in a Child & Cryptic Septic Endocarditis and Systemic Thromboembolism Triggered by Oral Microflora & Contribution of Hybrid SPECT CT Imaging with [99mTc] Tc-MDP in Battered Woman Syndrome](https://sjoranm.com/public/journals/2/cover_issue_26_en.jpg)
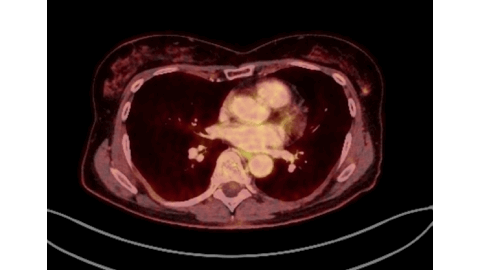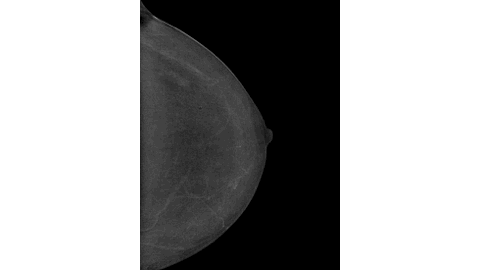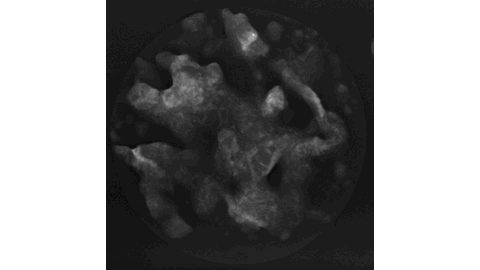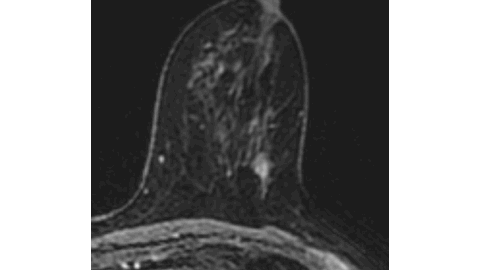
Marked FDG Uptake on PET/CT Corresponding to Low-Grade Ductal Carcinoma In Situ of the Breast: A Case Report - Denmark
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v23i1.14
This case demonstrates that a focal isolated area of increased FDG uptake on PET-CT should not be disregarded, even if no corresponding lesion is identified on second-look ultrasound.
Low-grade DCIS (Van Nuys Grade 1) may show FDG activity on PET-CT despite its subtle nature.
------------------------------------------------------------
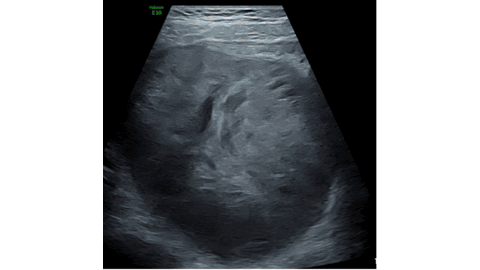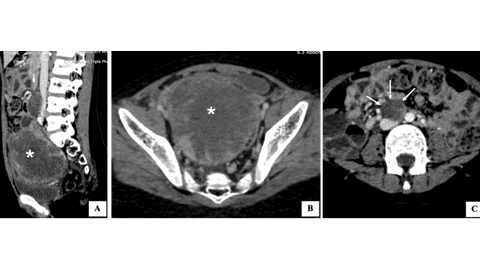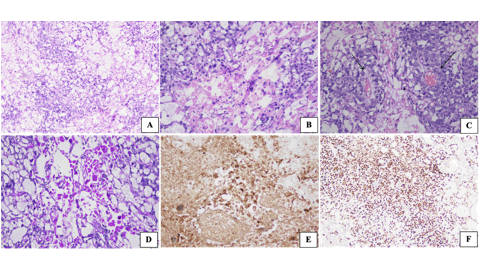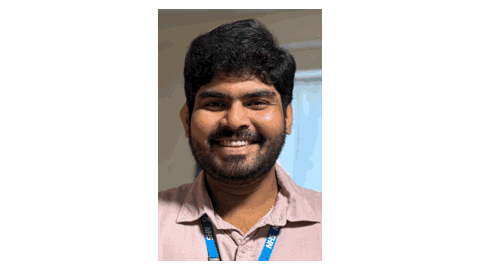
Malignant Yolk Sac Tumor of the Ovary Presenting as Adnexal Torsion in a Child: A rare Case Report with Review of Literature - United Kingdom & India
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v23i1.18
Introduction: Malignant yolk sac tumor is a rare ovarian neoplasm with peak incidence in young women. Its occurrence in children less than 10 years old is extremely uncommon. In this manuscript we report a rare case of malignant yolk sac tumor presenting with adnexal torsion, emphasizing the role of multimodality imaging in management.
Case Presentation: A 9-year-old female child was brought with the complaints of acute right lower quadrant pain, nausea and vomiting. On examination, the abdomen was tender with guarding. Laboratory investigations revealed leukocytosis, raised inflammatory markers and markedly elevated alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) levels. Ultrasonography revealed a mixed echogenic tumor in the right adnexa with features of adnexal torsion. Cross sectional imaging confirmed the presence of a heterogeneously enhancing tumor in the right adnexa with pelvic and paraaortic lymphadenopathy. Subsequently, the child underwent emergency laparotomy for adnexal detorsion with tumor excision. Postoperative histopatho-logical examination confirmed malignant yolk sac tumor.
Conclusions: This case underscores the rare presentation of ovarian malignant yolk sac tumor as adnexal torsion in a child and the role of multimodality imaging in its management.
------------------------------------------------------------
Cryptic Septic Endocarditis and Systemic Thromboembolism Triggered by Oral Microflora - USA
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v23i1.16
This unique clinical case underscores the pathogenic nature of oral commensal microbial flora such as Streptococcus Anginosis in provoking infective endocarditis of physiologically normal native heart valves despite the absence of priming systemic risk factors. Understanding the triggering events for this pathological transformation of Stroptococcus Anginosus in normal patients is very much necessary. This will allow the clinicians to anticipate this transpiration in the clinical settings and execute appropriate therapeutic measures to minimize the morbidity and mortality.
------------------------------------------------------------
Contribution of Hybrid SPECT CT Imaging with [99mTc] Tc-MDP in Battered Woman Syndrome - Morocco
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v23i1.20
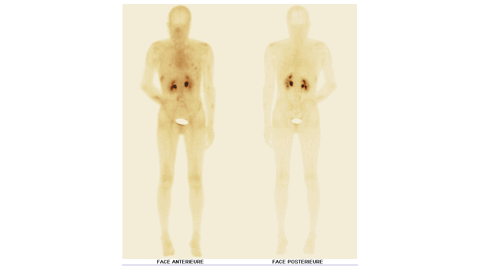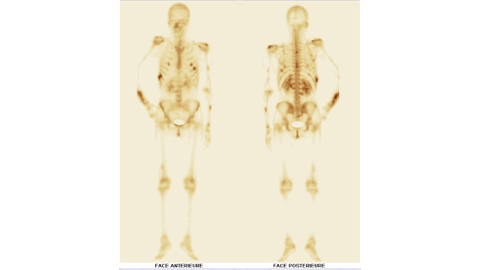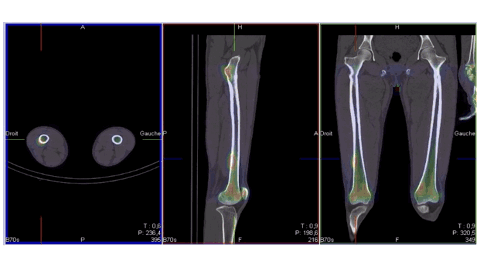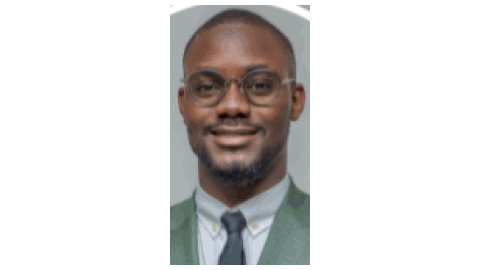
Introduction: Violence against women is a widespread health problem that knows no racial or social boundaries. It is generally difficult for forensic investigators to obtain medical evidence of violence, particularly in cases where the victims are assessed several months after the event. Bone scintigraphy can be used to identify and document trauma related to acts of torture, and it can also serve as valid evidence in court.
Case report: The bone scan revealed multiple areas of tissue uptake in the early phase, associated with bone uptake in the late phase involving both the axial and peripheral skeleton. In addition, several areas of bone uptake were observed in the late phase without corresponding tissue uptake in the early phase. The scintigraphic pattern demonstrated that the patient's bone lesions were of different ages. Based on these findings, early tissue uptake associated with late bone uptake was consistent with recent post-traumatic lesions, whereas late bone uptake without early tissue uptake was consistent with old post-traumatic lesions. The distribution of certain skeletal lesions suggested a defensive posture adopted by the victim.
Conclusion: In the context of a forensic investigation, bone scintigraphy is a valuable tool that not only detects bone lesions in patients suspected of physical assault, whether or not they present clinical signs, but also helps to determine when the injury occurred.