The Contribution of Bone Scintigraphy in benign bone pathology
Illustrations of Cases from the Nuclear Medicine Department at the University Hospital of FES
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v7i1.12Keywords:
Bone Scintigraphy, Benign bone pathology, hybrid SPECT/CT, topographical diagnosis, quantification and monitoring of bone lesionsAbstract
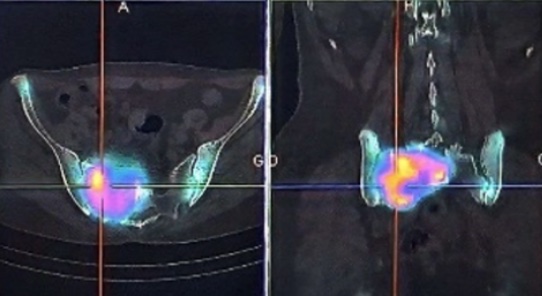
This work provides an overview of the effectiveness of bone scintigraphy and its role in diagnosing various benign conditions in the Nuclear Medicine Department of the University Hospital of Fez. It analyzes the criteria for selecting scintigraphy as a diagnostic tool and outlines the principles, key features, and protocols involved. These details support clinicians in confirming their diagnostic reasoning when evaluating musculoskeletal lesions or bone abnormalities, guiding their choice of imaging modalities. Clinicians initiate the diagnostic process by identifying relevant clinical factors and areas of uncertainty, leading to a preliminary diagnosis. Subsequently, nuclear physicians tailor the scintigraphy examination to address the specific clinical concerns. It's important to note that the clinical cases presented serve as illustrative examples rather than definitive benchmarks for image quality or equipment settings. They are intended to stimulate individual reflection based on each unique clinical scenario.
References
- M. Dumont *, C. Côté : La scintigraphie osseuse en trois phases pancorporelles, novembre 2012, ELSEVIER MASSON
- P. Granier *, M. Mourad : Exploration des polyalgies par la scintigraphie osseuse planaire couplée à la TEMP-TDM, octobre 2010, ELSEVIER MASSON
- Parisi MT, Otjen JP, Stanescu AL, et al. Radionuclide imaging of infection and inflammation in children: a review. Semin Nucl Med 2018 ; 48:148–65.
- Frédéric Paycha, Société française de médecine nucléaire et imagerie moléculaire (SFMN), Guide pour la rédaction de protocole pour la scintigraphie osseuse, Médecine Nucléaire 36 (2012) 687-697.
- A. Matrane , A. Guensi , M. Kebbou, Histiocytose langerhansienne osseuse multifocale : intérêt de la scintigraphie osseuse planaire, Médecine Nucléaire 36 (2012) 730-735
- https://www.universalis.fr/encyclopedie/technetium/2-technetium-et-imagerie-medicale/
- Guide du don usage de l’amylose cardique de L'ASNC et de L'EANM
- Résumé des caractéristiques du produit ANSM - Mis à jour le : 02/07/2008
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Assia Seddouki, Dr Sofia Chkikar, Essomada KPEKPEOU, Dr Mehdi Goudira, Pr Nadia Imaili Alaoui

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This license requires that reusers give credit to the creator. It allows reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format, even for commercial purposes.