The Radiology Display Technology
Progress Over Time and the Role of Standards Today
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.59667/sjoranm.v21i1.28Keywords:
digital image information chain, PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System), electronic devices with suitable displays, projectors, beamers, computer screens, tablets, televisions, smartphones, diagnostic significance, digital revolution from 1987 to 2025Abstract
Not long ago, X-ray information was recorded on film. Consequently, after development and fixation, post-processing of the image as we use today was simply only possible through another X-ray exposure with additional radiation and uncertain results. The introduction of the digital image information chain from the X-ray detector to the monitor has fundamentally changed this.
The digital transformation of radiology has been continuously expanded and improved through the application of new and increasingly powerful technical components. The omnipresence of radiological image information extends from the place of creation via PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System) not only within the radiology department but also throughout the entire hospital and its departments, such as emergency room, operating room, wards, and outpatient clinics of the referring specialties.
Further dissemination of digital image information occurs via CD, DVD, USB sticks, and via the internet through patient and referrer portals. The end display devices of the image recipients/users can be projectors, beamers, computer screens, tablets, televisions, smartphones, or other electronic devices with suitable displays. In fact, visualizations of X-ray images on not-too-large displays like smart-phone displays or like displays of car radios are conceivable, for example, if a WhatsApp image message arrives via mobile phone to a radiologist driving a car.
Following the desires of the regulatory authorities, all these displays would have to be continuously checked for their display quality because it cannot be ruled out that an X-ray image might be displayed. Theoretically, this is conceivable. However, it is simply not feasible in our overregulated reality by now.
Fact-based arguments are discussed regarding this issue, covering various aspects of the diagnostic significance and the technical physical specifications of radiological images. Thus, we provide lawmakers and authorities with evidence-based facts to ensure that future legislative measures appropriately regulate radiologic display quality. Or even better: No need for regulations at all !?
References
1. Reabal N. Digital Frontiers in Healthcare: Integrating mHealth, AI, and Radiology for Future Medical Diagnostics. In: Dr. Thomas FH, Prof. Charles ED, eds. A Comprehensive Overview of Telemedicine. Rijeka: IntechOpen; 2024:Ch.1. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.114142
2. Gupta S, Johnson EM, Peacock JG, et al. Radiology, Mobile Devices, and Internet of Things (IoT). Journal of Digital Imaging 2020;33(3):735-746. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-019-00311-2
3. Silosky MS, Marsh RM. Performance characteristics and quality assurance considerations for displays used in interventional radiology and cardiac catheterization facilities. J Appl Clin Med Phys 2018;19(5):708-717. https://doi.org/10.1002/acm2.12433
4. Lee CI, Gupta S, Sherry SJ, et al. Translating New Imaging Technologies to Clinical Practice. Acad Radiol 2018;25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acra.2017.03.027
5. Kovacs MD, Burchett PF, Sheafor DH. App review: management guide for incidental findings on CT and MRI. J Digit Imaging 2018;31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-017-0035-x
6. ESR paper on the proper use of mobile devices in radiology. Insights Imaging 2018;9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13244-017-0589-7
7. Giardino A, Gupta S, Olson E, et al. Role of Imaging in the Era of Precision Medicine. Acad Radiol 2017;24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acra.2016.11.021
8. O'Connell TimothyW, Patlas MichaelN. Mobile devices and their prospective future role in emergency radiology. The British Journal of Radiology 2016;89. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.20150820
9. Mervak BenjaminM, Davenport MatthewS, Flynt KelseyA, Kazerooni EllaA, Weadock WilliamJ. What the Patient Wants: An Analysis of Radiology-Related Inquiries From a Web-Based Patient Portal. Journal of the American College of Radiology 2016;13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacr.2016.05.022
10. Greco G, Patel AS, Lewis SC, et al. Patient-directed Internet-based Medical Image Exchange: Ex-perience from an Initial Multicenter Implementation. Acad Radiol 2016;23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acra.2015.10.012
11. Graetz I, Gordon N, Fung V, Hamity C, Reed ME. The Digital Divide and Patient Portals: Internet Access Explained Differences in Patient Portal Use for Secure Messaging by Age, Race, and Income. Med Care 2016;54. https://doi.org/10.1097/MLR.0000000000000560
12. Sandhu RS. Radiology Physics 300 App Review. J Digit Imaging 2015;29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-015-9858-5
13. Lewis Thomas Lorchan, Aungst Timothy Dy, Hutchinson Charles. Radiology education, mobile technology and medical apps. BMJ Simulation and Technology Enhanced Learning 2015;1. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjstel-2014-000009
14. Choudhri AF, Chatterjee AR, Javan R, Radvany MG, Shih G. Security Issues for Mobile Medical Imaging: A Primer. Radiographics 2015;35. https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.2015140039
15. Richardson Michael L. Audience Response Tech-niques for 21st Century Radiology Education. Aca-demic Radiology 2014;21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acra.2013.09.026
16. Dams FE, Leung KY, van der Valk PH, Kock MC, Bosman J, Niehof SP. Technical and radiological image quality comparison of different liquid crystal displays for radiology. Med Devices (Auckl) 2014; 7:371-7. https://doi.org/10.2147/MDER.S67443
17. Berkowitz SethJ, Kung JustinW, Eisenberg RonaldL, Donohoe Kevin, Tsai LeoL, Slanetz PriscillaJ. Resident iPad Use: Has It Really Changed the Game? Journal of the American College of Radio-logy 2014;11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacr.2013.04.017
18. Yoo JH. The meaning of information technology (IT) mobile devices to me, the infectious disease physi-cian. Infect Chemother 2013;45. https://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2013.45.2.244
19. Wojtczak Jacek, Bonadonna Peter. Pocket mobile smartphone system for the point-of-care subman-dibular ultrasonography. The American Journal of Emergency Medicine 2013;31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2012.09.013
20. Szekely A, Talanow R, Bagyi P. Smartphones, tablets and mobile applications for radiology. Eur J Radiol 2013;82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2012.11.034
21. Rodrigues MA, Visvanathan A, Murchison JT, Brady RR. Radiology smartphone applications; current provisions and cautions. Insights Imaging 2013;4. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13244-013-0274-4
22. Mickan S, Tilson JK, Atherton H. Evidence of effectiveness of health care professionals using handheld computers; a scoping review of systema-tic reviews. J Med Internet Res 2013;15. https://doi.org/10.2196/jmir.2530
23. Goldzweig CL, Orshansky G, Paige NM, et al. Electronic Patient Portals: Evidence on Health Outcomes, Satisfaction, Efficiency, and Attitudes: A Systematic Review. Ann Intern Med 2013;159. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-159-10-201311190-00006
24. Gerard P, Kapadia N, Acharya J, Chang PT, Lefkovitz Z. Cybersecurity in radiology: Access of public hot spots and public Wi-Fi and prevention of cybercrimes and HIPAA violations. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2013;201. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.12.9651
25. Bedi Harprit S, Yucel Edgar K. “I Just Bought My Residents iPads… Now What?” The Integration of Mobile Devices Into Radiology Resident Education. American Journal of Roentgenology 2013;201. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.13.10674
26. Al-Hasani H. Smartphone applications for the radiologist. Open J Radiol 2013;3. https://doi.org/10.4236/ojrad.2013.34037
27. Wallace S, Clark M, White J. ‘It’s on my iPhone’: attitudes to the use of mobile computing devices in medical education, a mixed-methods study. BMJ Open 2012;2. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2012-001099
28. Siddiqui A, Dreyer KJ, Gupta S. Meaningful use -A call to arms. Acad Radiol 2012;19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acra.2011.11.008
29. Mosa AS, Yoo I, Sheets L. A systematic review of health care apps for smartphones. BMC Med Inform Dec Mak 2012;12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6947-12-67
30. Demaerschalk BM, Vargas JE, Channer DD, et al. Smartphone teleradiology application is success-fully incorporated into a telestroke network environ-ment. Stroke 2012;43. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.112.669325
31. Vinson DD. No more paper Tiger: Promise and Peril as HIPAA Goes HITECH. J Healthc Risk Manag 2011;30. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhrm.20058
32. Njuguna Njogu, Flanders AdamE, Kahn CharlesE. Informatics in Radiology: Envisioning the Future of E-Learning in Radiology: An Introduction to SCORM. RadioGraphics 2011;31. https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.314105191
33. Ahern DK, Woods SS, Lightowler MC, Finley SW, Houston TK. Promise of and Potential for Patient-Facing Technologies to Enable Meaningful Use. Am J Prev Med 2011;40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amepre.2011.01.005
34. Krupinski EA, Becker GJ, Laszakovits D, Gerdeman AM, Evanoff MG. Evaluation of off-the-shelf displays for use in the American Board of Radiology main-tenance of certification examination. Radiology 2009;250(3):658-64. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2503080596
35. Indrajit IK, Verma BS. Monitor displays in radiology: Part 2. Indian J Radiol Imaging 2009;19(2):94-8. https://doi.org/10.4103/0971-3026.50819
36. Indrajit I, Verma B. Monitor displays in radiology: Part 1. Indian J Radiol Imaging 2009;19(1):24-8. https://doi.org/10.4103/0971-3026.45341
37. Sparacia Gianvincenzo, Cannizzaro Floreana, D’Alessandro Donna M, D’Alessandro Michael P, Caruso Giuseppe, Lagalla Roberto. Initial Ex-periences in Radiology e-Learning. RadioGraphics 2007;27. https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.272065077
38. Geijer H, Geijer M, Forsberg L, Kheddache S, Sund P. Comparison of color LCD and medical-grade monochrome LCD displays in diagnostic radiology. J Digit Imaging 2007;20(2):114-21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-007-9028-5
39. Rowell Melissa R, Corl Frank M, Johnson Pamela T, Fishman Elliot K. Internet-Based Dissemination of Educational Audiocasts: A Primer in Podcasting—How to Do It. American Journal of Roentgenology 2006;186. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.05.1315
40. Navarro-Sanchis Eugenio L, Sendra-Portero Fran-cisco. Informatics in Radiology (infoRAD). Radio-Graphics 2005;25. https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.251045057
41. Kazan B. New electronic displays and their possibilities for radiology. Invest Radiol 1989; 24(10):817-9. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004424-198910000-00018
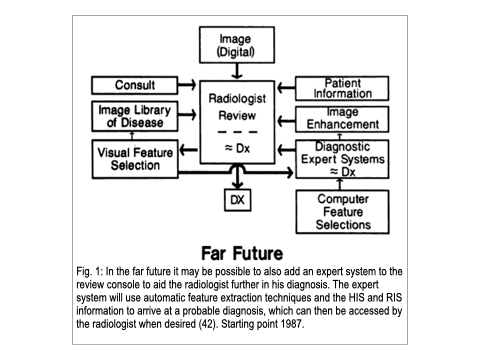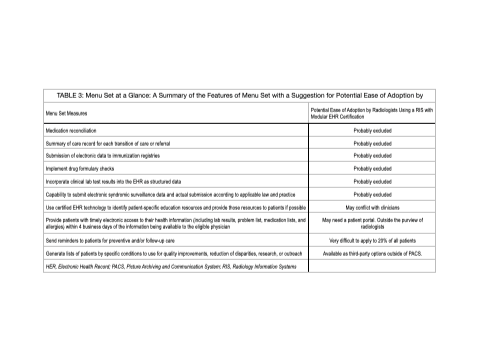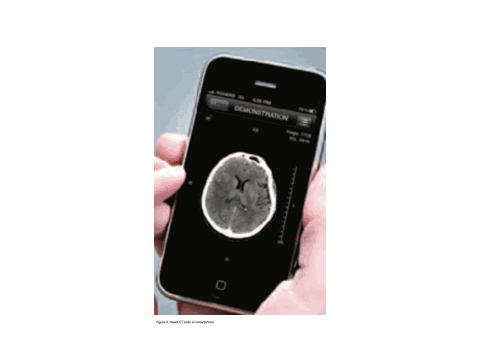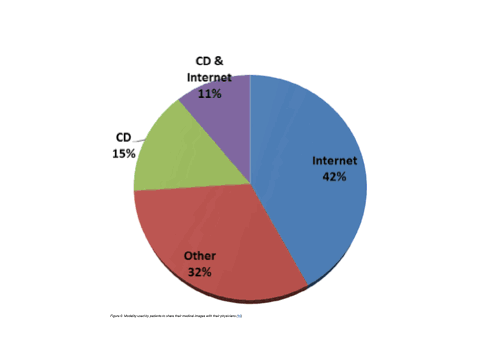
42. Seeley GW, McNeill K, Dallas WJ. Displays in radiology: past, present, and future. Radiographics 1987;7(6):1261-6. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiographics.7.6.3423332
Downloads
Published
Data Availability Statement
none
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Dr. med. Frank Mosler, Prof. Dr. med. Gerd Nöldge

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This license requires that reusers give credit to the creator. It allows reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format, even for commercial purposes.